Enterprise Generative AI Adoption: Risk Evaluation for Competitive Advantage | Blog
The adoption of generative AI technology poses four major types of threats to enterprises: data privacy and security, reliability and explainability, responsibility and ownership, and bias and ethics. By assessing current risk levels and implementing practices, tools, and systems to manage these challenges, enterprises can realize the most value from this transformative technology. Learn more about evaluating generative AI risk to gain an edge in this blog. Learn more about our Generative AI Risk Assessment.
Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) has captivated popular imagination like nothing else, promising a future filled with endless possibilities. For the first time, this technology can create art, synthesize human voices, and generate human-like responses to questions.
Open AI’s ChatGPT triggered the mainstream adoption of generative AI, racking up more than 100 million monthly active users within just two months of its launch. Today, more than 300 startups are developing various generative AI-related applications.
Enterprises globally have recognized generative AI’s emergence as a watershed moment and are scrambling to identify the best way to leverage its capabilities. Numerous use cases across industries and functions have already emerged and are being piloted.
Many technology providers have incorporated generative AI as an integral part of their solutions, and others are forging relevant partnerships to jump on the bandwagon.
However, while many organizations are excited about long-term generative AI adoption, few fully consider the potential risks. In this blog, we will delve deeper into the importance of generative AI risk assessment.
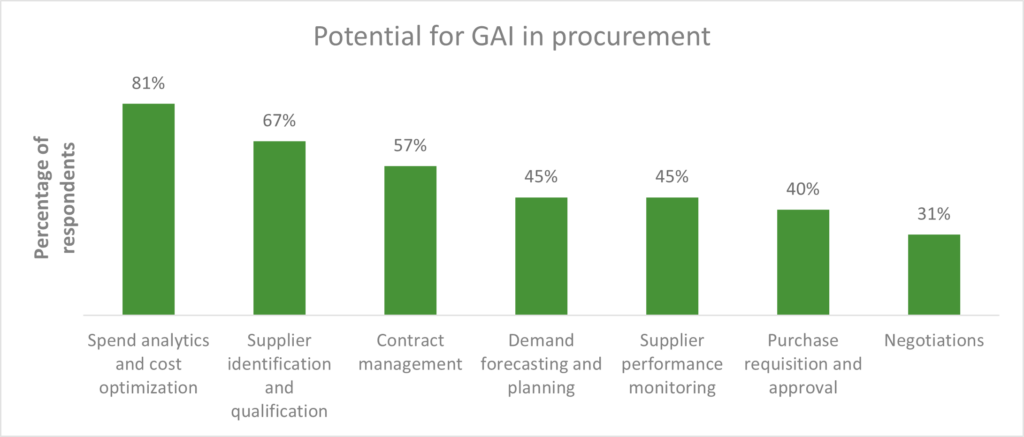
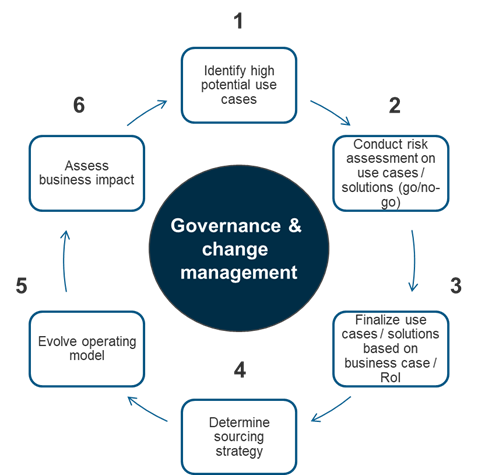
To realize maximum value from generative AI adoption, enterprises must undertake a structured incremental approach (as illustrated in Figure 1). This framework involves prioritizing use cases, assessing adoption risks, identifying suitable providers, adapting existing operating models, providing effective governance and change management, and reviewing performance against expectations.
Generative AI risks
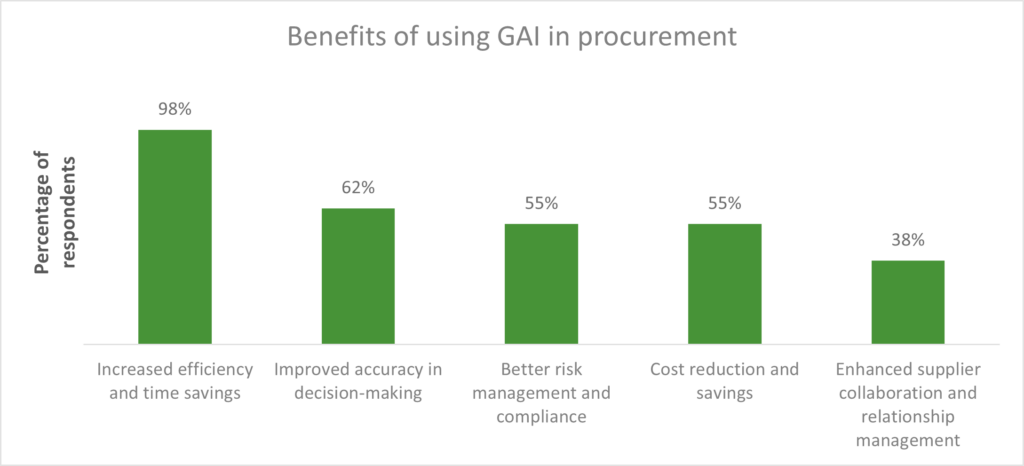
Generative AI’s ease of usage has accelerated its adoption, highlighting both its value and its risks. Broadly, generative AI risks can be grouped into four categories: data privacy and security, reliability and explainability, responsibility and ownership, and bias and ethics (as shown below in Figure 2).
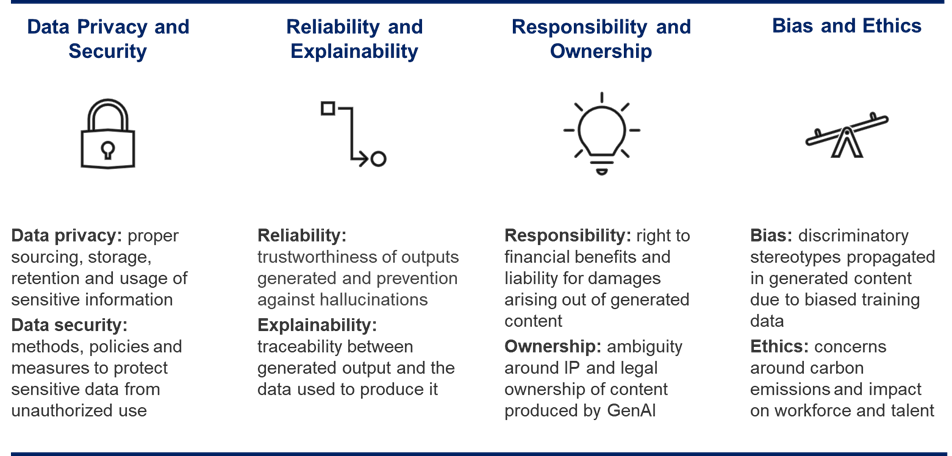
Let’s look at how these risks typically manifest and some examples:
Data privacy and security: Regulatory fallout from undisclosed data collection and retention is a key issue with generative AI models. This stems from the practice of developing AI models that can address a broad range of topics, rather than training data for a specific purpose. Further concerns include employees inadvertently sharing confidential enterprise data through user prompts or training data. In some cases, unfiltered prompts may allow employees access to data beyond their purview. From a cyber threat perspective, generative AI raises the risk of data breaches through malware, phishing, and identity theft
| Samsung employees pasted confidential source code into ChatGPT to look for errors and optimize the data, inadvertently adding it to ChatGPT’s training data pool that can possibly be accessed by others. |
Reliability and explainability: The quality and representativeness of training data greatly influence the accuracy of output produced by generative AI models. Deficiencies in the training data manifest as errors in generated content that may have serious legal ramifications beyond eroding customer trust. Furthermore, in the absence of required information, generative AI models may even fabricate information to answer a question. This leads to a false sense of expertise and can mislead the average user. Without a confidence score that estimates the likely accuracy of the generated content or some other equivalent mechanism, enterprises will need to develop and operationalize fact-checking of AI-generated content
| During Microsoft’s Bing chat demo, the search engine was asked to analyze earnings reports from Gap and Lululemon and in comparing its answers to the actual reports, the chatbot missed some numbers and made some up. |
Responsibility and ownership: The legal ownership of a piece of content produced by generative AI raises complex questions. Does it belong to the enterprise that licensed the generative AI product or the company that owns the generative AI product? Moreover, do individuals or organizations whose content was used to train the AI model partially own any subsequent content produced by the AI? These legal quandaries currently lack clear answers. An evident problem is generative AI producing output that contains distinct and identifiable pieces of Intellectual Property (IP) owned by others. This can lead to potential legal fallout for the entity that deployed the generative AI model. Enterprises need to work with their legal teams to evolve their IP management amid widespread generative AI adoption
| “Zarya of the Dawn” is a graphic novel written by Kris Kashtanova who used an AI based image generation software called Midjourney to create illustrations for the novel. After having initially given full copyright protection for the novel, the US Copyright Office later restricted the copyright to only the text and the arrangement of the illustrations and not the illustrations themselves. The justification provided was that copyright protection could only extend to human creators. |
Bias and ethics: An AI trained on biased data will propagate those biases, potentially leading to the generative AI producing discriminatory and stereotypical content. Failing to identify and preemptively remove such content through effective moderation can lead to severe reputational and legal ramifications for the enterprise and the generative AI provider.
Widespread generative AI adoption has the potential to ramp up carbon emissions from training and operating AI models. This can have significant implications for an enterprise’s Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals
| In a study conducted by Bloomberg on Stable Diffusion (an AI-based text-to-image software), the rendering of more than 5,000 images for people with high- and low-paying jobs was full of racial and gender stereotypes. The results indicated men and individuals with lighter skin tones accounted for most high-paying roles. |
How can enterprises assess their risk exposure to generative AI?
While the risks emanating from generative AI usage are notable, its benefits are too significant for enterprises to ignore. Consequently, enterprises that can leverage generative AI’s strengths while effectively mitigating its risks will outperform their peers. To effectively draw up a risk management plan for generative AI, enterprises need to first assess their current risk exposure to generative AI.
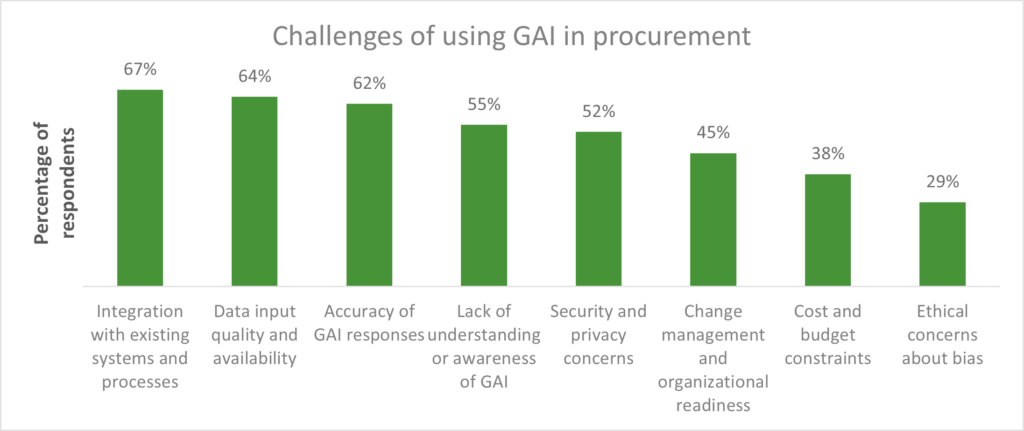
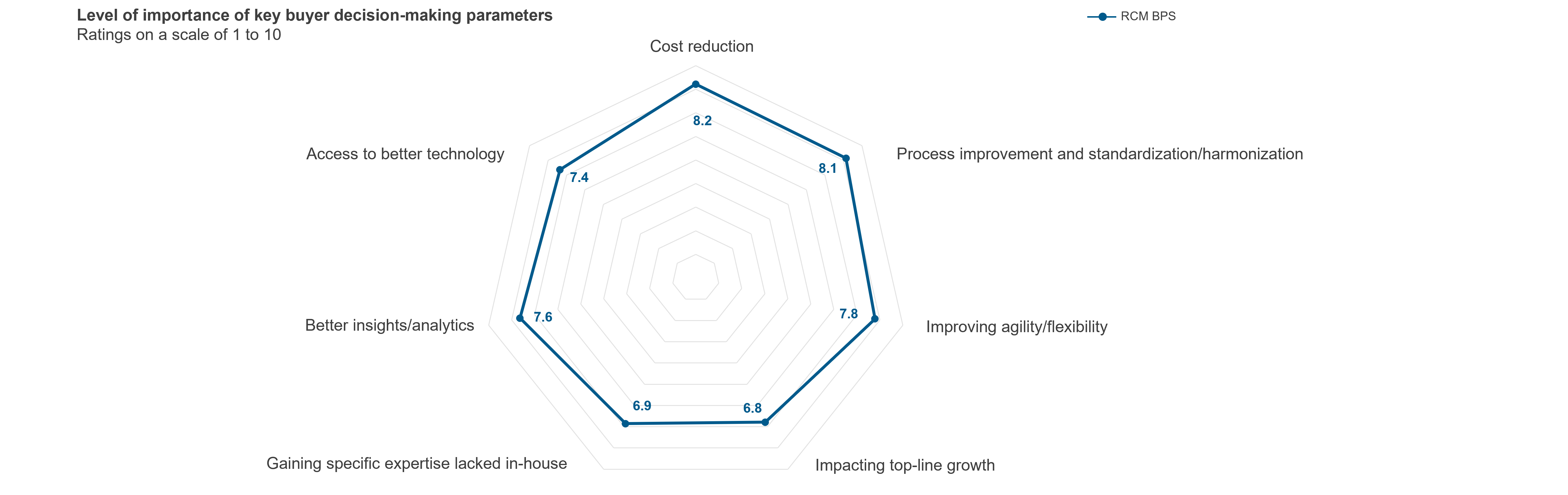
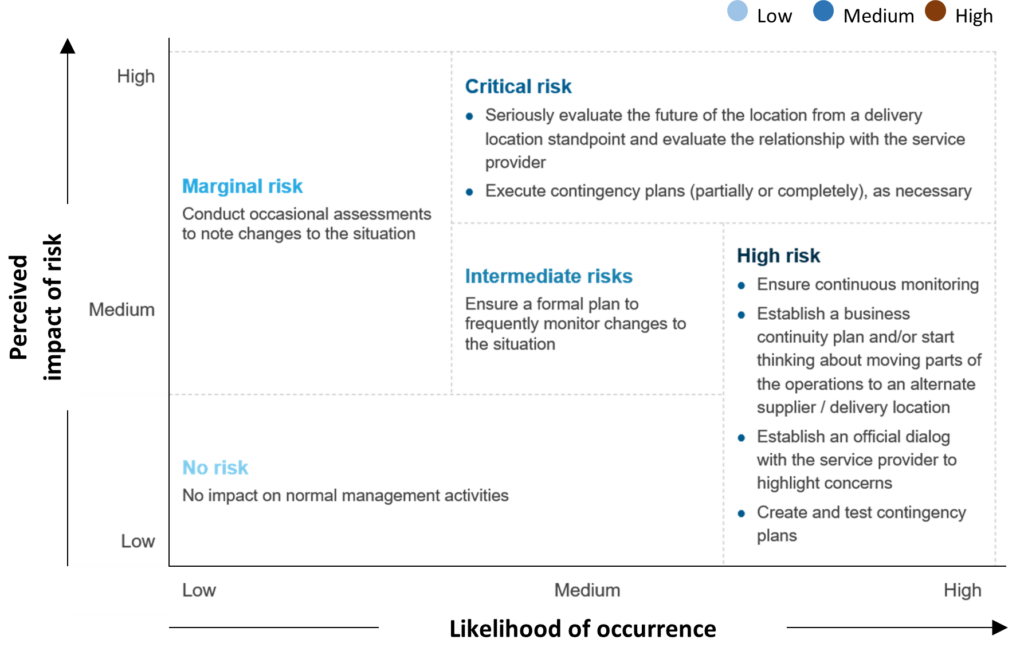
Everest Group has developed a multi-dimensional risk assessment framework (see Figure 3) to help enterprises take stock of their current risk profile for generative AI adoption. This framework is deployed through a tool that comprises 21 questions spanning the four risk categories mentioned above.
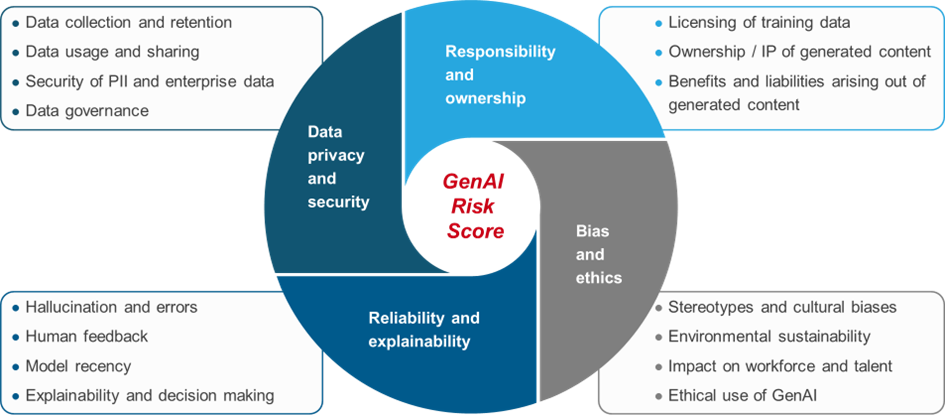
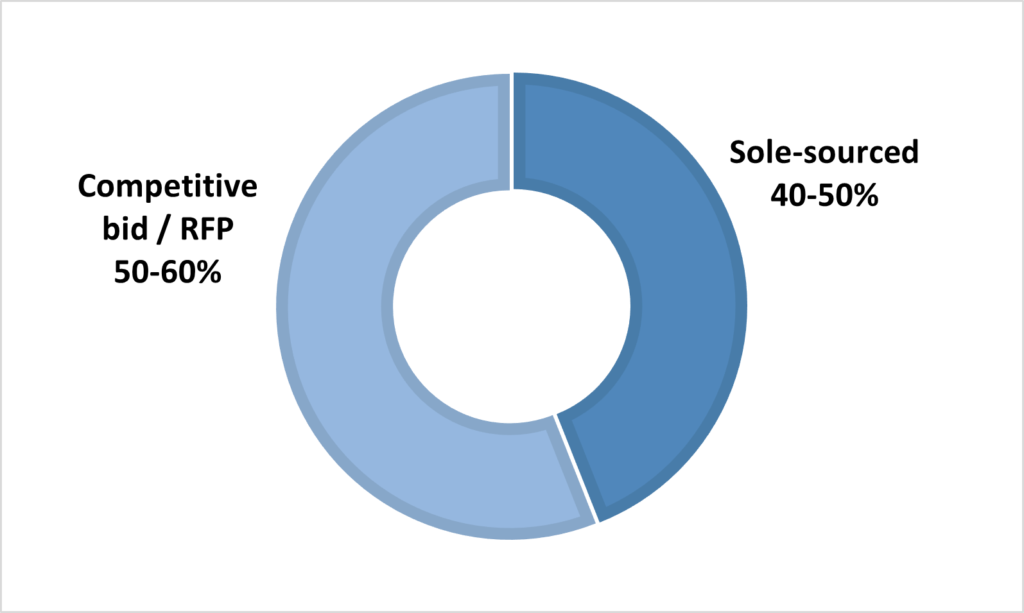
Responses provided by the enterprise across the four categories are weighted and aggregated to arrive at a risk score (see Figure 4).

Evaluating the risk exposure from generative AI is a necessary step to successfully implement and leverage generative AI to create value for customers. Incorporating appropriate risk management practices, tools, and mechanisms in the generative AI ecosystem can instill the confidence needed to take bigger bets, create differentiation, and fully harness this transformative technology.
Deploy our Generative AI Risk Assessment Tool. To discuss this tool and generative AI adoption strategies, please reach out to: [email protected], [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected].
Check out our 2024 Key Issues webinar, Key Issues 2024: Creating Accelerated Value in a Dynamic World, to learn the major concerns, expectations, and trends for 2024 and hear recommendations on how to drive accelerated value from global services.