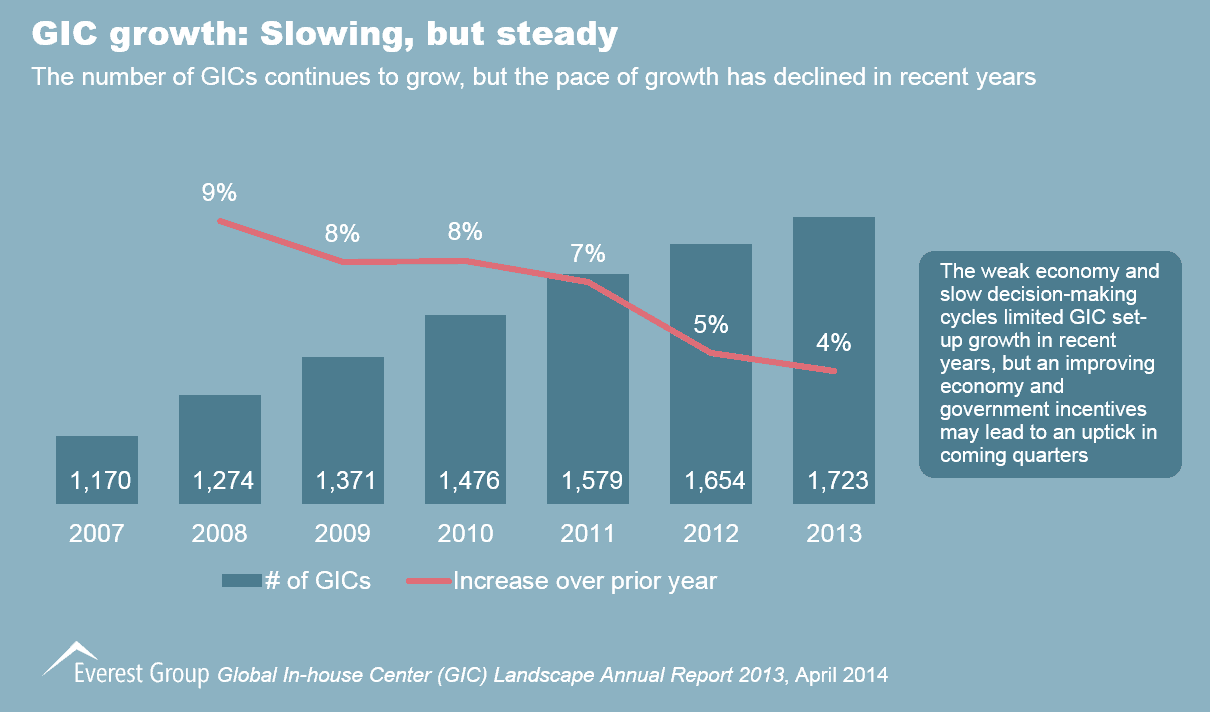
The Global In-house Center (GIC, formerly referred to as captives) market was once thriving with unprecedented statistics – 97 new GIC set-ups in 2009, 105 in 2010, and 103 in 2011. Then there was a dip, with only 75 new centers in 2012, and 69 in 2013. This, coupled with numerous acquisitions of GICs by service providers, (e.g., KBC Group’s financial arm by Cognizant, Bayer’s Indian IT operations by Capgemini, and Hutchison Whampoa’s India-based call center operations by Tech Mahindra), is likely to raise questions and concerns about the future of the in-house model.
Let us look at the ground realities of the GIC model’s growth and evolution:
- Indeed, the rate of growth of GIC set-ups has slowed down. However, this can largely be attributed to a weak economic scenario and slow decision-making cycles, and should not be construed as weakening confidence in the GIC model. As the future outlook of the global economy is positive, we expect the GIC market to gain momentum in the near future
- Established GICs are evolving in their journey to be a partner of their parent firms, rather than just an offshore cost-saving entity
- The success of the GIC model in pioneer delivery locations such as India and the Philippines is leading buyers to explore and diversify to other locations
- CEE countries are witnessing increased activity due to aggressive government incentives, the language advantage, and the nearshore proposition
- Relatively untapped regions in the Middle East and Africa reported an astonishing eight GIC set-ups in the last year alone
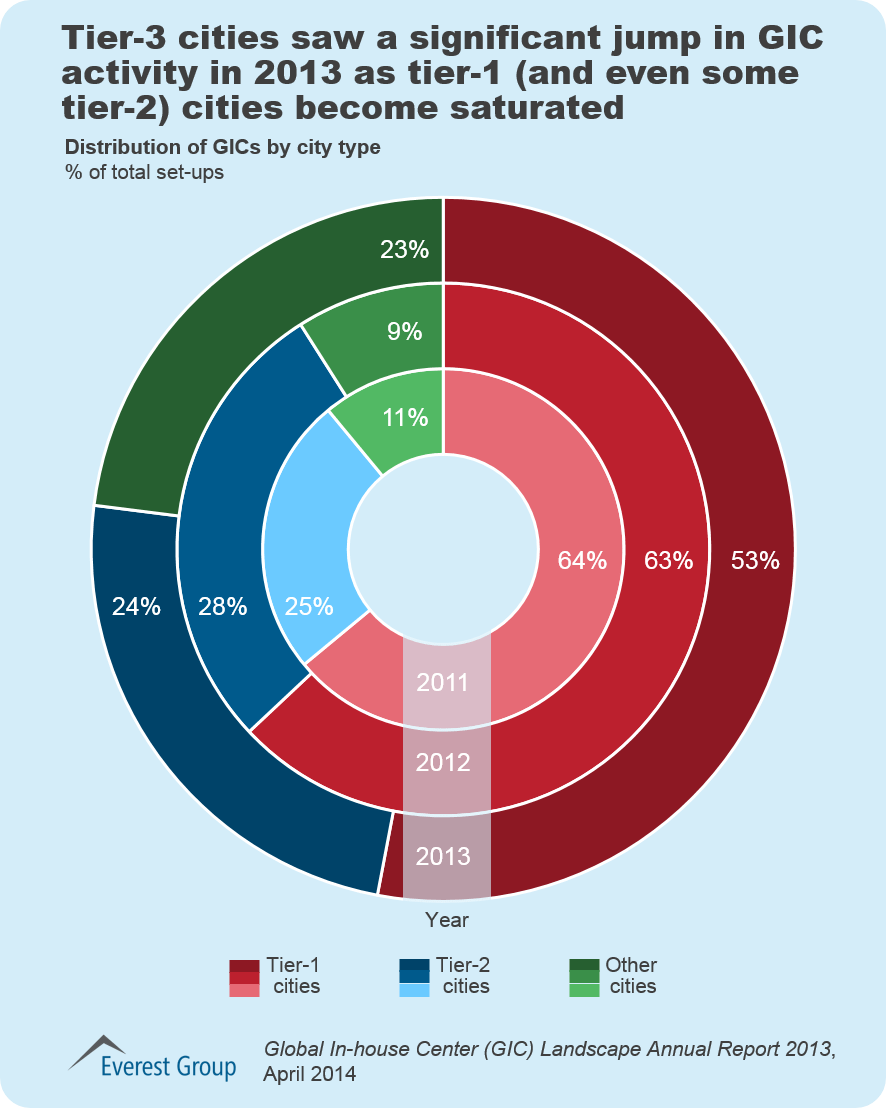
- Firms are expanding their GIC operations to tier-2 and 3 cities due to saturation in tier-1 cities in mature locations such as India
- While the technology, manufacturing, distribution and retail, and BFSI industries continue to have a strong foothold, other verticals – such as conglomerates, business services, hospitality, and printing and publishing – have emerged to gain a noticeable share of the GIC market.
Further, while buyers’ moves from an outsourced to an in-house model rarely receive considerable fanfare, they do paint a picture of the health of the GIC model. For example, HP had been General Motor’s main IT vendor per a US$2 billion contract awarded in 2010, but in 2012 the automaker decided to insource a huge amount of its services as part of its new strategy, leaving HP with only a few. AstraZeneca plans to reduce its outsourcing work, which is currently spread across multiple Indian software service providers. BT plans to have more control of its processes by taking back its outsourcing contracts from service providers, and increasing its capacity in existing shared services centers in India and Malaysia.
The bottom line is that while GIC set-up growth may be slowing, the model continues to be an integral component of organizations’ sourcing strategy. Firms continue to leverage both sourcing models (service providers and GICs) based on best fit with their sourcing needs, cost and value objectives, and services demand profile.
For more insights on the GIC model landscape, please refer to our recently released report “Global In-house Center (GIC) Landscape Annual Report 2013.” The report provides a deep-dive into the GIC landscape and a year-on-year analysis of the GIC trends in 2013, comparing them with trends in the last two years. The research also delivers key insights into the GIC market across locations, verticals, and functions, and concludes with an assessment of strategic priorities for GICs.










