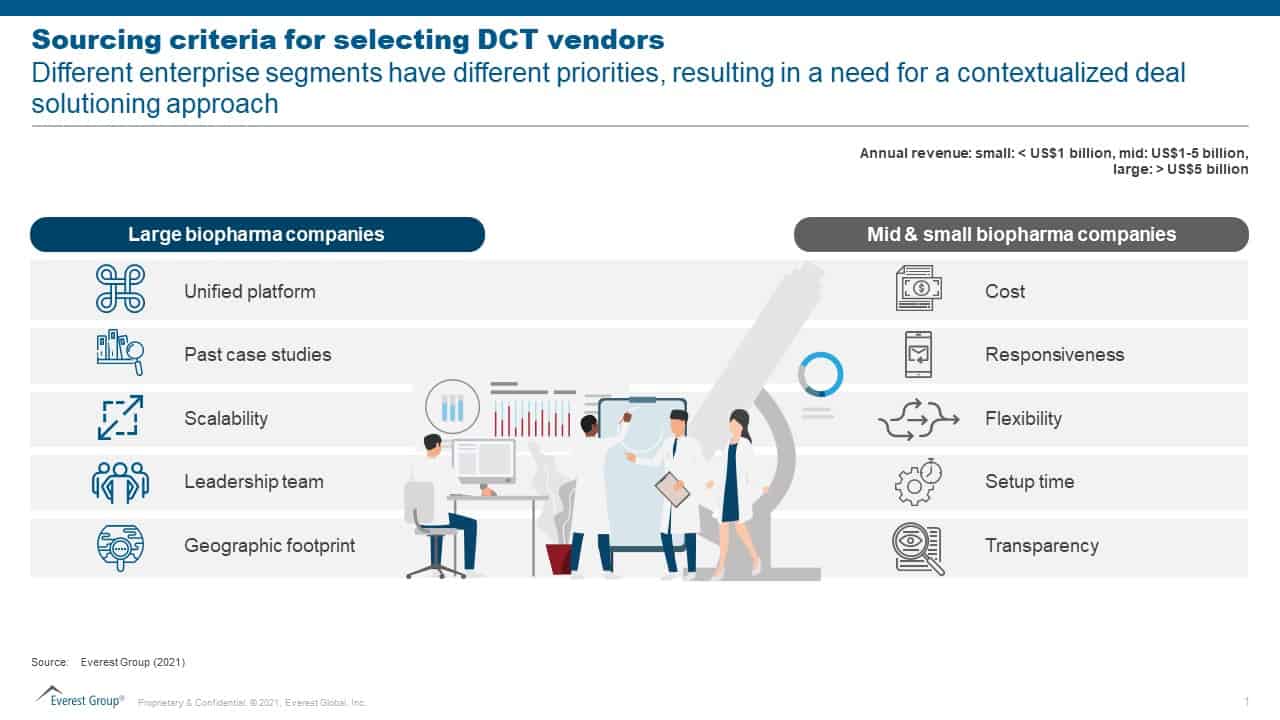
Blog
Agentic AI – Exploring its Enterprise Potential

The emergence of agentic AI represents the next frontier in AI-based automation, offering enterprises the opportunity to revolutionize work processes through increased autonomy, enhanced decision-making capabilities, and greater adaptability. But can it move from consumer applications to the enterprise environment? Read on to explore agentic AI’s potential to transform operations and the challenges of this rising technology.
Enterprises today increasingly prioritize generative AI (gen AI) to enhance individual knowledge and assist employees. However, newer models, such as agentic AI, are emerging as promising solutions that can make decisions and fulfill goals. While agentic AI shows considerable potential, can it be adapted from consumer use cases to enterprise workflows? Let’s explore this further.
What is agentic AI?
Agentic AI is a new evolution that enables end-to-end task execution through natural language-based inputs. It goes beyond retrieving information or increasing knowledge and can take action with minimal human oversight.
For example, gen AI can help employees write code for tasks. Agentic AI takes this to the next level by running, debugging, and executing the code to achieve the desired outcome. Ultimately, agentic AI promises to combine the reasoning, execution, and course correction mechanisms humans typically use to accomplish goals, as illustrated below:
The early promise of agentic AI has been demonstrated in consumer use cases through practical tools such as Auto-GPT and innovative AI devices such as rabbit r1. These applications show that when pushed to its limit, agentic AI can significantly reduce the reliance on multiple applications/products for distinct workflows, achieving actions simply through chat interfaces. This offers a glimpse into agentic AI’s potential for transforming enterprise workflows.
Given the potential agentic AI has demonstrated in a business-to-consumer context, it is intriguing to consider how this technology could be applied in an enterprise setting. At the lower end of the realization spectrum, it could more effectively automate mundane or repetitive tasks with limited human supervision. On a larger scale, agentic AI could be leveraged to have fully autonomous agents that think through and achieve outcomes and goals communicated in natural language. Regardless of the promise eventually realized, agentic AI will likely boost employee productivity and provide greater end-to-end automation.
Agentic AI in the enterprise
Currently, agentic AI seems somewhat more elegant in a consumer use case. In an enterprise environment, automated dynamic workflow generation and execution pose risks for multiple reasons, including the cost of error (such as incorrect workflows) and enterprise technology complexity.
However, given the potential benefits, it is unsurprising that multiple tech vendors – from prominent tech providers to early-stage startups – are working on building platforms and solutions that enable agentic AI in the enterprise.
Despite workarounds and solutions that are being developed for these risks, agentic AI in an enterprise environment encounters the following obstacles:
- Explainability: For critical processes in particular, the ability to explain why a specific workflow was generated to solve a problem is essential
- Supervision: Fully automated execution of dynamically generated workflows may be problematic in many enterprise circumstances. Agentic AI will require human review for generating workflows and often for execution and handling exceptions
- Ecosystem complexity: With the many products and solutions within the enterprise landscape, generating and executing workflows tailored to specific ecosystems will require specialized training and execution tools/interfaces
- Governance and security: As is the case with any automation, agentic AI will also need robust governance, privacy, security, audit mechanisms, and other guardrails
What does this mean for existing automation tools?
In the near future, Agentic AI will likely augment existing automation tools, not replace them. Agentic AI can work with automation tools in certain situations to enable smoother execution. For instance, data and insights gained through task mining can be used to train and refine the agentic AI model for workflow generation. This model, embedded within a process orchestration tool, can then be used to build workflows that are subsequently executed using application programming interfaces (APIs), robotic process automation (RPA), intelligent document processing (IDP), and other automation tools.
What does the future hold?
Although using fully autonomous agents may appear to be a magical remedy to the software sprawl problem, it is hardly that simple. Even if users could generate and execute workflows instantaneously in an enterprise environment, mechanisms to trace actions, capture related data, and enable the right access levels to different user groups are necessary.
In the near future, it is improbable that agentic AI will threaten larger systems designed to address high-value enterprise use cases. Nonetheless, agentic AI will undoubtedly simplify and enable goal achievement and end-to-end execution, shortening the time to productivity for new users. As both core technology and guardrail mechanisms improve, multi-vendor point solutions with incremental benefits may become unnecessary due to agentic AI’s efficiency.
While still a nascent technology, agentic AI has the potential to be adopted more quickly in an enterprise environment due to its functions and benefits. As the technology and ecosystem rapidly advance over the next few years, we will monitor the progress and adoption. Follow this space for more insights, and contact Anil Vijayan at [email protected] to discuss further.
Watch the event, Distinguishing Gen AI Hype from Real Applications, to learn about practical applications shaping the future of intelligent technologies.