Blog
Building Purpose-driven Gen AI – Why We All Have a Role to Play in the Future Success of the Gen AI Ecosystem

Gen AI’s rapid adoption is evident from its early success; for example, ChatGPT 3.5 amassed one million users within five days of its 2022 launch, and now has over 180 million users – these numbers simply can’t be ignored! Organizations across industries are now leveraging gen AI to transform operations, enhance decision-making, personalize customer experiences, and foster innovation. However, this rapid adoption comes with significant environmental and social challenges. Our analysts have delved deeper into the topic, to decipher how and why gen AI needs to be nurtured and understood throughout every ‘step of the ladder’ in the marketplace. Reach out to discuss this topic in depth. The current landscape: The environmental footprint of gen AI is notable; generating a response from gen AI uses six to ten times more energy than traditional internet searches, exacerbating the information technology (IT) carbon footprint in every sector. Socially, gen AI also faces issues such as bias and ethical concerns, with biases in gen AI outputs perpetuating discrimination and misinformation. The particular concern around fair use doctrine is also emerging, with the New York Times suing OpenAI to use its news articles without permission, to train its model. To address these multifaceted challenges, it is crucial to understand the roles of various stakeholders in the gen AI ecosystem. Each plays a distinct part in promoting sustainability and mitigating negative impacts. The gen AI’s ecosystem involves various stakeholders—technology providers, service providers, enterprises, regulatory bodies, and research/coalition building organizations. Technology providers can enhance model efficiency and inclusivity, while service providers develop energy-efficient and responsible artificial intelligence(AI) solutions. Enterprises, as end users, can demand sustainable practices and influence market demand. Regulatory bodies also play a crucial role by establishing and enforcing standards and regulations. Meanwhile, research and coalition building organizations drive innovation and offer insights into emerging best practices and technologies for sustainable gen AI. Together, these stakeholders form a cohesive ecosystem essential for advancing sustainability in the gen AI landscape.
Everest Group explores how key stakeholders influence gen AI’s path to sustainability
At Everest Group, we view gen AI’s sustainability through the lens of the planet and people. To ensure a sustainable future for gen AI, we have identified three themes:
- Decarbonization and energy management: Reducing energy consumption and lowering the carbon footprint of gen AI technologies.
- DEIB (Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Belonging): Promoting inclusive and equitable practices within gen AI development and deployment.
- Accessibility: Ensuring gen AI technologies are accessible and usable for everyone, regardless of their disability status.
Three stakeholders—technology providers, service providers, and enterprises—are pivotal in translating these mandates into practical actions. Understanding their contributions is essential for advancing gen AI sustainability. Technology providers, service providers, and enterprises are directly involved in implementing and influencing sustainable practices, making their involvement critical for tangible progress. While regulatory bodies, governments, and research organizations and industry coalitions play a complementary part by establishing standards, regulations, and guiding research, the immediate impact on sustainability stems from the actions and commitments of these primary stakeholders. Everest Group has developed an assessment framework to define the roles the primary stakeholders play in making gen AI more sustainable. Our ROLE framework evaluates how much pressure existing AI regulations place on stakeholders, their operational control across the gen AI value chain (from conceptualization to end-of-life), their leadership in partnerships and engineering research & development (ER&D), and their expertise in shaping sustainable gen AI. The ROLE framework is depicted in Exhibit 1. 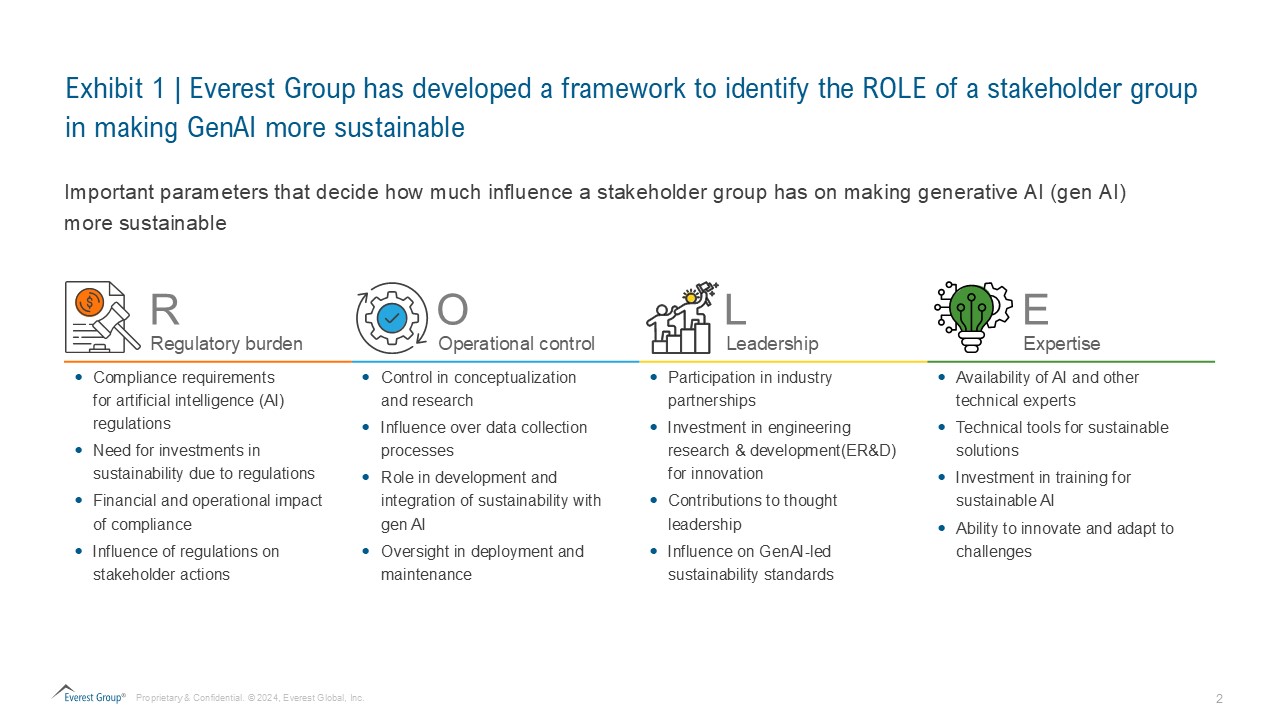 After scoring the three stakeholders across the parameters defined in our ROLE framework, our assessment has categorized stakeholders into three roles:
After scoring the three stakeholders across the parameters defined in our ROLE framework, our assessment has categorized stakeholders into three roles: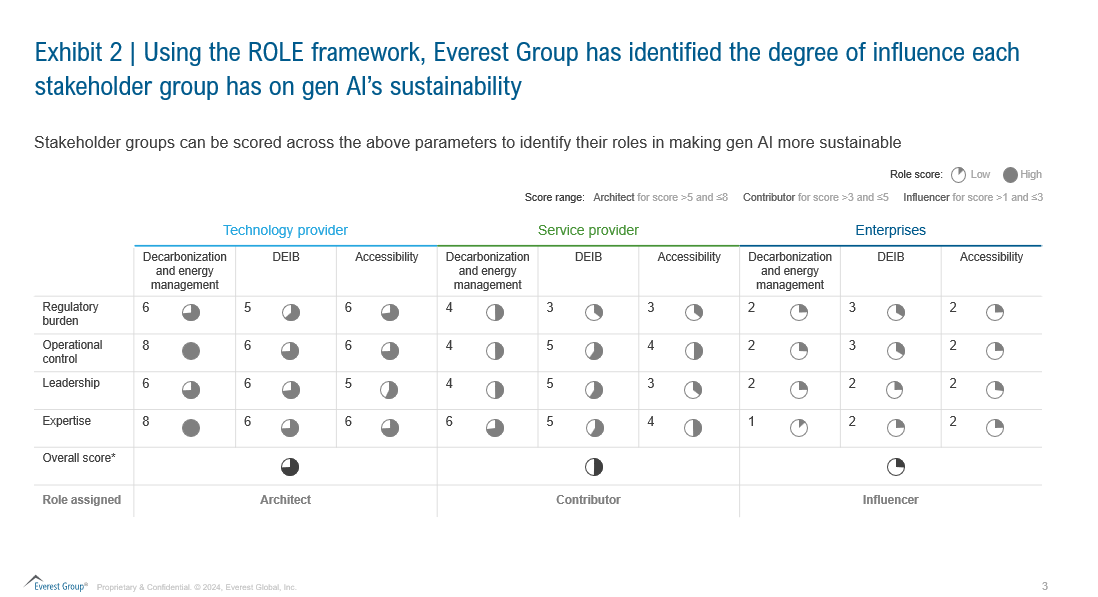
- Architect: Reflects stakeholders with high engagement and significant influence on advancing gen AI sustainability.
Technology providers are currently in the role of Architect. They drive innovation and set the standards for sustainable gen AI technologies. Their involvement spans the entire lifecycle of gen AI, from development to deployment, and they are at the forefront of integrating sustainability into their solutions.
- Contributor: Indicates stakeholders who actively support and engage with sustainability efforts but do not lead them.
Service providers fall into the Contributor category. They play a vital role in implementing and supporting sustainable practices within gen AI solutions, yet their influence is more supportive rather than leading the charge in sustainability initiatives.
- Influencer: Denotes stakeholders who monitor or follow sustainability developments with minimal direct involvement but may shape discussions and perceptions through their observations.
Enterprises are classified as Influencers. While they adopt gen AI solutions, their involvement in driving sustainability is limited. They largely follow industry trends without actively shaping or leading sustainability efforts. However, they can shape the demand for more sustainable gen AI through discourse, forming industry-coalitions to adopt best practices, or co-innovating sustainable gen AI solutions with tech partners.
The ROLE framework provides a comprehensive assessment of the market and the contributions of various stakeholders. It categorizes stakeholders based on their overall impact within the ecosystem. However, we recognize that some players are making exceptional efforts that could elevate their roles—from Influencers to Contributors or from Contributors to Architects. This nuanced view acknowledges that individual players can surpass their general category and assume a more influential position in driving sustainability. The evolving roles of technology providers, service providers and enterprises present valuable opportunities for further advancements. By exploring these dynamics, we can better understand how each stakeholder can contribute to a more sustainable gen AI ecosystem. Everest Group will keep digging deeper to understand the gen AI sustainability ecosystem better. Stay tuned for our upcoming blogs, where we’ll explore strategies for tackling gen AI’s complex sustainability challenges. We’ll delve deeper into each stakeholder’s evolving role and offer insights on bridging the gaps in their current efforts. If you found this blog interesting, check out our recent blog focusing on Unleashing The Power Of Advanced AI Engines: Transforming Business Operations For The Future | Blog – Everest Group (everestgrp.com), which delves deeper into the topic of advance AI and gen AI. If you have questions or want to discuss these topics in more depth, please contact Meenakshi Narayanan, Rita N. Soni and Cecilia Van Cauwenberghe.