Blog
Generative AI in Marketing: The Sidekick You Never Knew You Needed

Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI)
can deliver efficiency and scale in content production, marketing support, and media channels like never seen before while also spurring innovation. Learn about the opportunities and obstacles of Generative AI in marketing in this blog.
Don’t miss the webinar, Welcoming the AI Summer: How Generative AI is Transforming Experiences.
“In my lifetime, I’ve seen two demonstrations of technology that struck me as revolutionary. The first time was in 1980, when I was introduced to a graphical user interface… The second big surprise came last year… from OpenAI… I knew I had just seen the most important advance in technology since the graphical user interface.” – Bill Gates
OpenAI’s introduction of ChatGPT onto the world stage heralded a seismic shift in the path toward intelligent automation. With its ability to create complex and innovative solutions, GAI has become the buzzword in boardrooms and strategy meetings. Enterprises are in an arms race to tap GAI through integrations, in-house development, and investments in start-ups.
Let’s look at its soaring popularity in the illustration below:
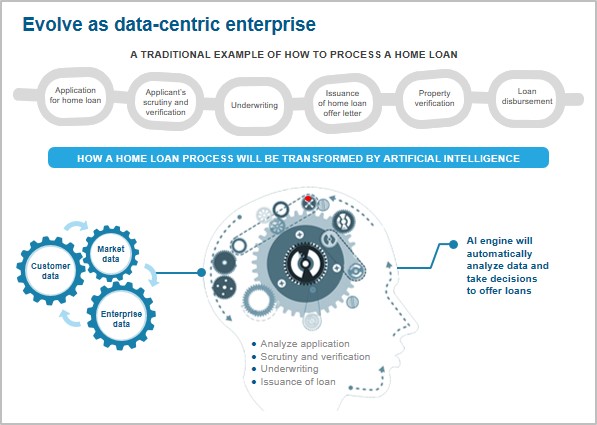
From healthcare to finance and from content creation to moderation, GAI has potential use cases cutting across almost every industry. Enterprises are eager to harness this groundbreaking technology’s power to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and unlock new opportunities.
What will the use of Generative AI in marketing mean?
With its impact spread across the marketing services value chain, GAI opens a novel world of possibilities, as illustrated below:
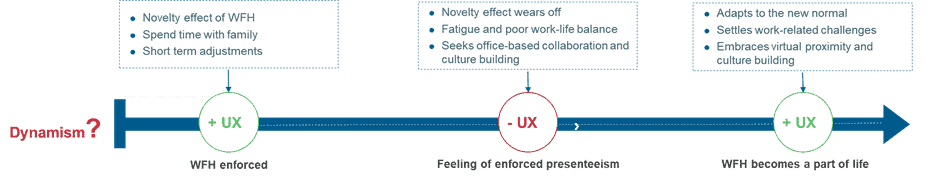
GAI proves to be efficient and effective in marketing services, particularly in content production, marketing support, and media channels. However, as with any emerging technology, it comes with concerns and challenges. Some of the implications and concerns are discussed below.
Content generation
Perceived implication:
GAI frees resources for other higher-level tasks that require human attention, such as strategic planning and community building.
Possible concern: Marketers need to weigh the time and efforts required to review and validate the content generated by GAI to ensure accuracy and consistency with brand messaging.
AI-assisted branding
Perceived implication:
GAI’s capabilities can improve digital media and also can impact traditional channels in areas of product ideation, branding initiatives, and advertising campaigns.
Possible concern: Despite aesthetic designs and descriptive language, consumers might not feel connected to the products without a sense-check from human input.
Search engine optimization (SEO) and organic search
Perceived implication:
Due to the conversational interface, the query results are highly pinpointed, raising the bar for enterprises to focus on contextually relevant content on their landing pages.
Possible concern: The new face of search marketing will rely heavily on AI technology, meaning marketers need to upgrade to real-time AI-driven and intent-based analysis for search to stay competitive.
Intent-driven search marketing
Perceived implication:
Search algorithms increasingly will be built around user-intent and intent-driven actions rather than keywords or links.
Possible concern: Instead of focusing on keywords and links as ranking factors, marketers will need to keep updated through intent analytics and stay relevant by providing users with the right information at the right time to drive conversion or engagement.
Lead generation
Perceived implication:
GAI can engage with website visitors in real time and help qualify them as leads based on their specific needs and interests. This can help sales teams focus efforts on the most promising leads and improve conversion rates.
Possible concern: Customer-facing GAI tools need to be accurate and handle queries without any biases. Since the answers offered are only as accurate as the training dataset, customer dissatisfaction is always a risk.
Sales enablement
Perceived implication:
GAI can provide sales teams with real-time data and insights on customer behavior, payment status, billing cycle, etc., enabling them to tailor sales pitches and ultimately lead toward revenue operations.
Possible concern: Access to consumer touchpoints and lack of transparency in the algorithms raises data privacy issues since whatever is fed into the AI is processed, stored, and re-utilized to improve query responses.
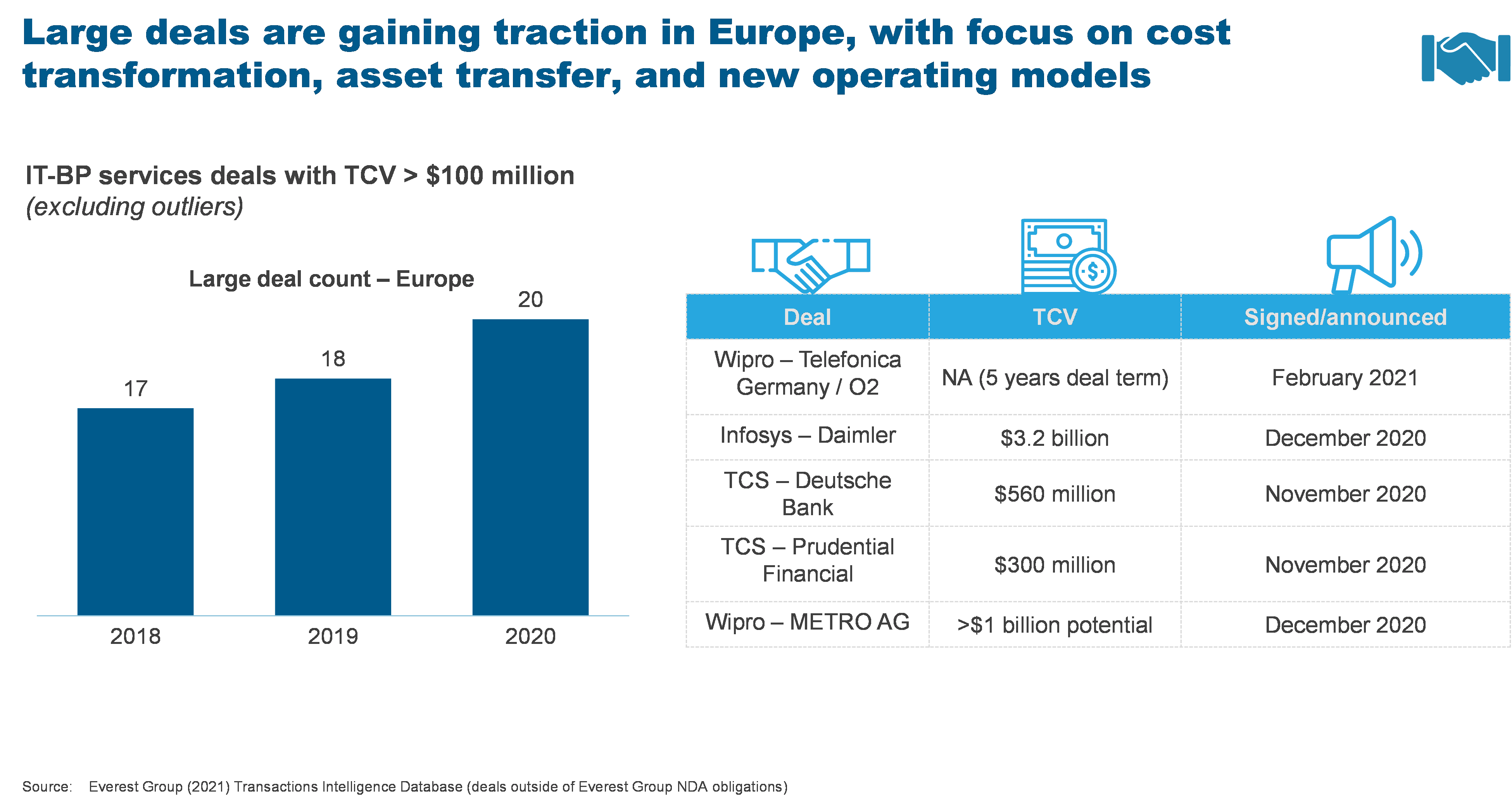
Exploring GAI: some novel use cases
As the market perspective is being developed, GAI is still in the test-and-play phase as enterprises and service providers have started experimenting with potential use cases like the ones below:
| AI content creation engine | Branding through Generative AI |
 |
 |
|
|
| Intelligent chatbots | Marketing and campaign support |
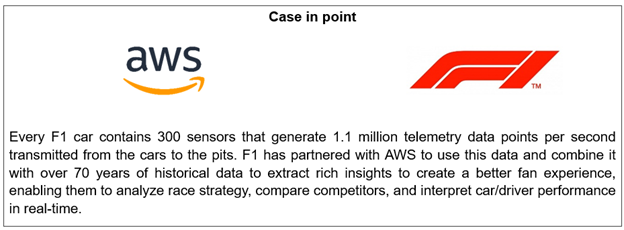  |
 |
|
|
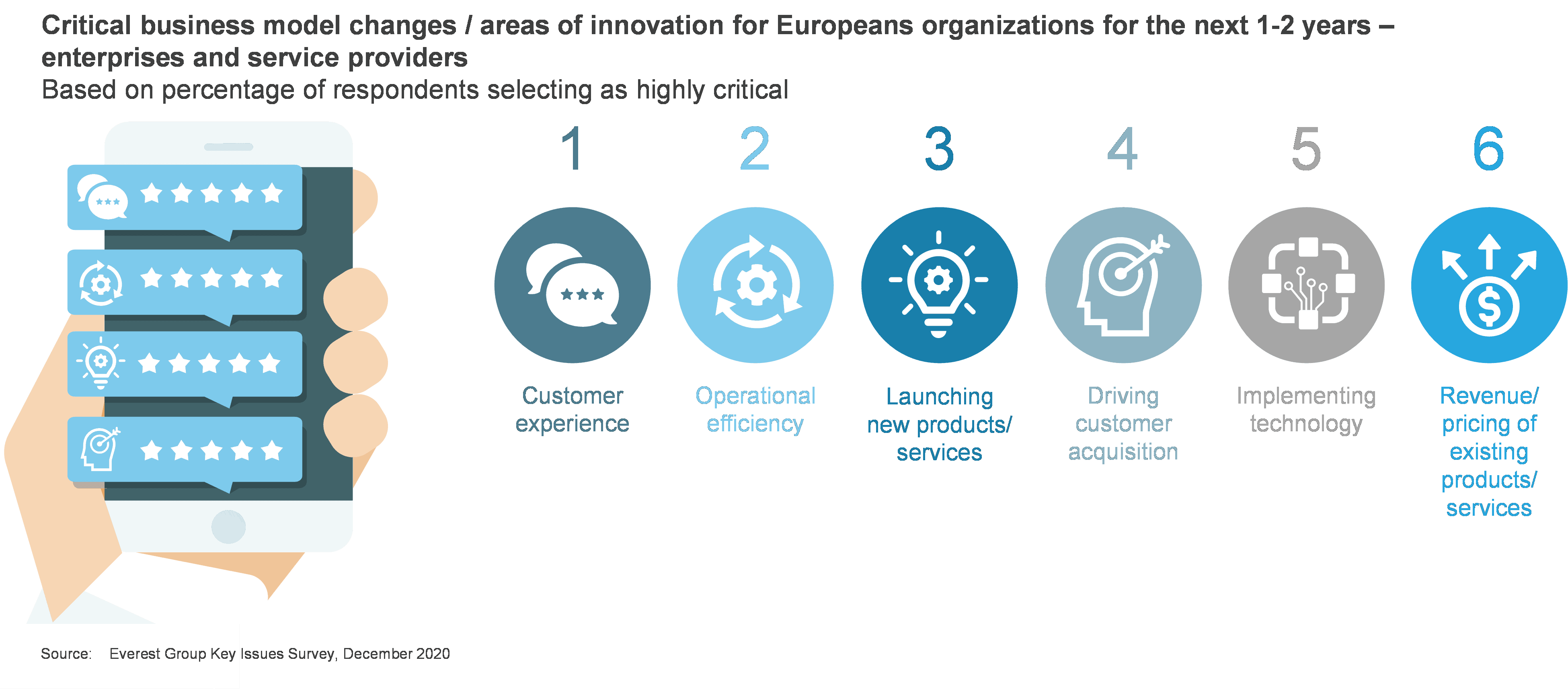
CMO compass: order out of chaos
Although many enterprises are using GAI as an exploration tool in marketing, realizing the business opportunity will require a customized Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) compass that can help create order out of chaos, as seen in the likeness below:
These four facets can act as the cardinal directions while navigating the GAI conversation.
GAI has rapidly transformed how content creation and marketing support are managed, showcasing a level of efficiency and scale that was previously impossible. In fact, by the time one finishes reading this blog, GAI likely handled hundreds or even thousands of queries and helped develop countless lines of content.
As this technology continues to evolve and mature, we can only expect its impact to grow, ushering in a new era of innovation. Enterprises must exercise prudence and careful consideration as they delve deeper into the potential applications of GAI. Ensuring that responsible implementation and ethical concerns remain at the forefront of their decision-making process is essential.
To discuss Generative AI in marketing, please contact Ravi Varun, or Nishant Jeyanth.
Learn more about Generative AI in marketing in, Generative AI – Redefining the Experience Design and Development Process.