Blog
Agentic AI: True Autonomy or Task-based Hyperautomation?

Agentic artificial intelligence (AI) has taken the world by storm, redefining how enterprises interact with customers and manage experiences. Agentic AI operates with full autonomy, continuously learning, adapting, and making intelligent decisions in real time.
But is it all true? When we peel back the layers of technological abstraction, a more nuanced reality emerges. Let’s find out.
Reach out to discuss this topic in depth.
From a Customer Experience Management (CXM) standpoint, agentic AI refers to AI-driven systems that autonomously manage customer interactions, adapt responses based on real-time context, and proactively resolve issues without requiring human intervention.
Unlike traditional AI chatbots or Interactive Voice Responses (IVRs) that follow predefined scripts, agentic AI can dynamically assess customer sentiment, predict intent, and personalize interactions across multiple touchpoints. These systems continuously learn from past interactions, optimize workflows, and escalate only extremely complex cases to human agents when necessary.
Positioned as a breakthrough in artificial intelligence, Agentic AI is seen as the next step toward fully autonomous digital operations, promising efficiency gains, cost reductions, and smarter decision-making. Enterprises are eager to explore its potential, while AI technology vendors race to showcase their latest advancements in agentic AI capabilities.
However, there exists a gap between how agentic AI is being currently made available in the market vs what it is truly capable of.
Guided autonomy v/s true independence
Agentic AI is being promoted as an autonomous system capable of independent decision-making, problem-solving, and self-improvement. However, the reality is different:
-
- Self-evolving workflows for different situations
-
- Hype: AI agents can autonomously initiate, execute, and complete tasks across systems without human intervention
-
- Reality: Most Agentic AI follows predefined workflows and relies on human-set goals, Application Programming Interface (API) calls, and trigger-based execution. They are not making independent choices but responding to programmed instructions
-
- No requirement of human supervision
-
- Hype: AI agents can replace human decision-makers and operate without supervision
-
- Reality: Even the most advanced AI agents today require human oversight, especially in dynamic environments where contextual understanding and ethical reasoning are needed. The human-in-the-loop model is still critical
-
- Proactive decision-making and task execution
-
- Hype: AI agents will proactively identify opportunities, solve problems, and take actions without needing explicit instructions
-
- Reality: AI agents are reactive, they execute tasks based on specific prompts or triggers but do not self-initiate new goals or dynamically adjust their strategies in the way humans do
-
- Seamless execution for complex tasks
-
- Hype: Agentic AI can handle complex, multi-domain problems and generalize across different industries and functions
-
- Reality: While agentic AI agents are highly efficient at ‘narrow’ tasks such as scheduling meetings, summarizing reports, and automating customer interactions, it lacks true cross-domain intelligence or reasoning required for ‘wide’ tasks that have multi-dimensional workflows
-
- Capability of independent reasoning
-
- Hype: AI agents can reason independently, break down complex problems, and strategize optimal solutions
-
- Reality: Agentic AI solutions are made of Large Language Model (LLM)-based prompt chaining, which means that they stitch together multiple prompts in a structured sequence rather than demonstrating true, self-generated reasoning
-
- Automatic assignment of goals without human intervention
-
- Hype: Agentic AI agents are self-evolving and assign goals according to the need of the situation
-
- Reality: These AI agents require external inputs such as APIs, databases, rules, or triggers to take actions. They do not self-assign goals but respond to the tasks for which they are created
The fundamental design characteristics of today’s AI agents is that its workflows are carefully designed, structured, and tuned by humans before deployment. It can automate processes, make decisions within a predefined scope, and even exhibit problem-solving capabilities in specific contexts. However, it cannot be seen as a fully autonomous AI system that can independently navigate an ever-evolving CXM landscape without guidance.
AI maturity framework: Assessing the current level of transformation and what the future holds
While true agentic AI represents the highest level of AI autonomy and business impacts in customer service, surpassing traditional automation, true autonomy is still an aspiration. The following maturity matrix illustrates the evolution of AI-based solutions in CXM, ranging from basic automation to fully autonomous, self-improving agentic AI models:
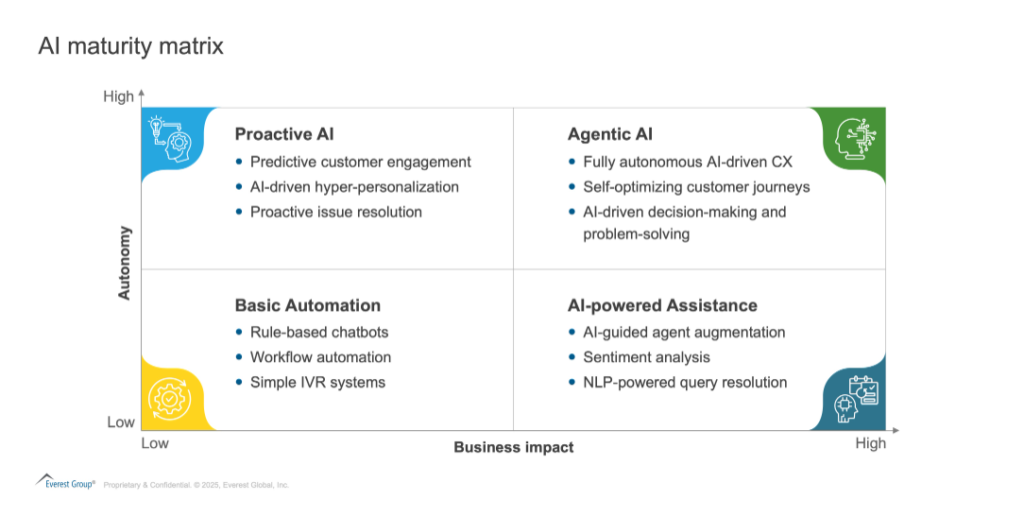
At present, the market has achieved an added layer of autonomy within the AI-powered assistance and proactive AI segments. However, true agentic AI, where systems can independently make decisions, learn from unstructured environments, and adapt dynamically without human intervention, is something we are steadily progressing toward.
While current agentic AI models rely on predefined parameters, supervised learning, and human oversight, ongoing advancements in reinforcement learning, self-improving algorithms, and multimodal AI are paving the way for more autonomous and adaptable systems.
Key considerations for enterprises
As the market steadily progresses toward towering AI-led business processes, enterprises must take a strategic and measured approach toward building agentic architectures. While innovation in Agentic AI presents new opportunities, its successful adoption requires a clear understanding of both its current capabilities and future potential.
To fully leverage AI while mitigating risks, organizations must focus on key factors that will shape their AI strategy and execution, including:
-
- Understand the level of current capabilities: Enterprises must recognize that agentic AI will not replace human decision-making across all functions with 100% autonomy. Instead, it will augment human capabilities within a controlled environment
-
- Operational dependencies: The success of agentic AI hinges on robust data governance, AI model training, and ongoing fine-tuning
-
- AI-driven process reengineering: Enterprises cannot simply deploy agentic AI and expect efficiency gains. They must rethink workflows, data integration, and decision hierarchies to extract real value from their investments
-
- Strategic orchestration to maximize human-AI synergy: The true value of agentic AI lies not just in automating tasks, but in enabling seamless coordination between AI agents, humans, and existing enterprise systems. Organizations should focus on building an orchestrated ecosystem where AI agents complement traditional rule-based automation and human expertise. A phased adoption approach will minimize risks, optimize Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) interventions, and allow enterprises to scale agentic AI in a controlled and strategic manner
The way forward
Truly autonomous Agentic AI, capable of independent decision-making, self-learning, and proactive problem-solving, remains an aspirational goal, but one that is within reach in the near to medium term.
Advances in multi-agent collaboration, reinforcement learning, and self-evolving models are rapidly closing the gap between today’s structured AI workflows and truly autonomous systems.
Emerging techniques, such as adaptive reasoning frameworks, self-directed goal-setting, and real-time contextual learning, are laying the foundation for AI, that can operate with minimal human oversight. While current implementations still rely on predefined workflows and human intervention, continuous innovation in AI architectures and decision-making models is accelerating progress toward true autonomy. With ongoing breakthroughs, enterprises may soon leverage AI agents that not only execute tasks, but also anticipate needs, refine their own logic, and evolve dynamically in complex environments.
If you found this blog interesting, check out our Agentforce Meets Gemini | Blog – Everest Group, which delves deeper into another topic regarding Experience, Sustainability & Trust.
If you have questions or want to discuss your AI adoption strategy further, please contact Anubhav Das [email protected], or Kartik Arora [email protected].
Additionally, enterprises seeking guidance on language translation offerings for CXM can gain valuable insights from our recently published Tech Vendor Spotlight: AI-powered Language Translation in Customer Experience Management (CXM). This report highlights an overview of AI-powered language translation offerings in CXM with detailed insights on technology vendors offering the same.
At Everest Group, we’re tracking the pulse of the market – and we want your input on how your business is reacting to the latest market uncertainties.
Please take 30 seconds to answer our 2-question poll and see how your perspectives align with your peers: https://lnkd.in/gaBXx5c7