Blog
Navigating the Agentic AI Tech Landscape: Discovering the Ideal Strategic Partner

As the agentic AI ecosystem evolves, so will its potential to deliver greater benefits which in turn will increase utilization and reliance on the technology, leading to widespread permeation. But enterprises have already started realizing the rewards and extraordinary accomplishments this technology promises to yield, including increased productivity, optimized workflow and improved decision making.
The early adoption pattern of agentic AI reflects a strong preference for horizontal use cases (Exhibit 1) with functions such as sales & marketing, customer support and HR leading the pack, though the industry-specific processes are also expected to pick up soon.
Reach out to discuss this topic in depth.
Exhibit 1: Adoption of agentic AI by business function Source: Everest Group (2024)  Emerging Agentic AI tech landscape The tech landscape for agentic AI is evolving rapidly. Everest Group’s Innovation watch assessment on agentic AI products (Exhibit 2) published in September 2024, mapped out the key agentic AI technology providers on their market performance and ecosystem drivers. While market performance is linked to the scale of operations and maturity of the product, ecosystem drivers include key partnerships and investments.
Emerging Agentic AI tech landscape The tech landscape for agentic AI is evolving rapidly. Everest Group’s Innovation watch assessment on agentic AI products (Exhibit 2) published in September 2024, mapped out the key agentic AI technology providers on their market performance and ecosystem drivers. While market performance is linked to the scale of operations and maturity of the product, ecosystem drivers include key partnerships and investments.
Exhibit 2: Everest Group innovation watch assessment for agentic AI products Source: Everest Group (2024) 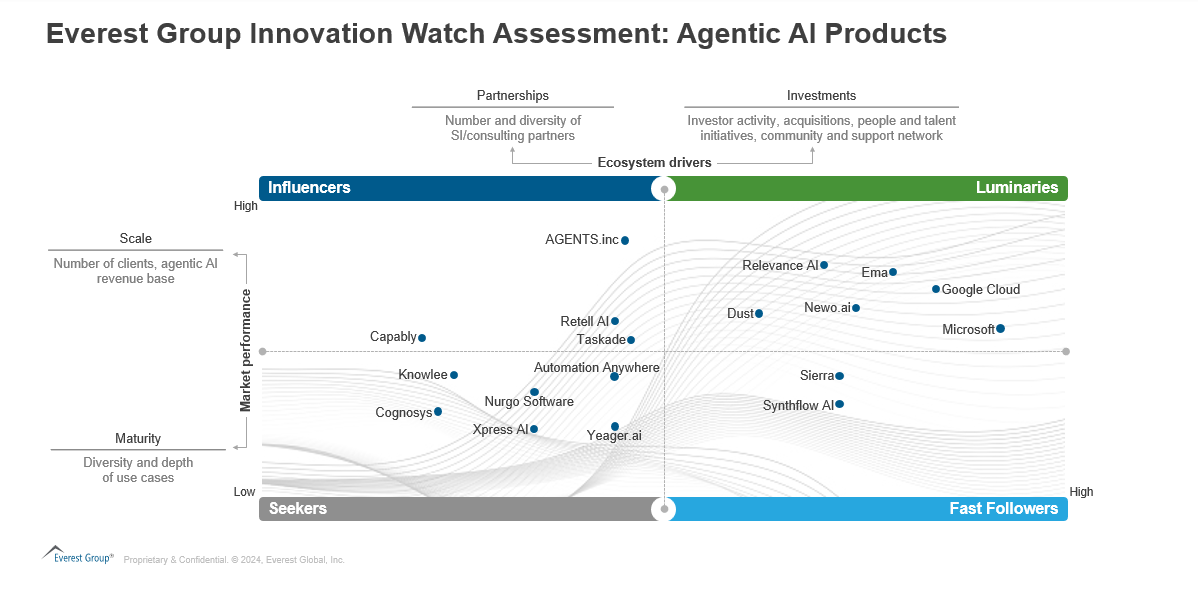 As you can expect, the pace of change and innovation in this budding market is very high. In the short time frame since this assessment was launched, many providers have made announcements or have ventured into this space. Some notable ones are:
As you can expect, the pace of change and innovation in this budding market is very high. In the short time frame since this assessment was launched, many providers have made announcements or have ventured into this space. Some notable ones are:
- Salesforce Agentforce: launched at Dreamforce 2024, Agentforce comes with multiple prebuilt agents such as sales development agents, sales coaches, personal shopping agents, service agents, and campaign agents. It also supports agent customization via Agent Builder, Model Builder, and Prompt Builder
- ServiceNow Xanadu: Agentic AI integration into the ServiceNow platform is expected to be available from November 2024 with Customer Service and information technology (IT) Service agents being the first in a set of agents that will continue to be added through 2025
- UiPath: Agent builder was launched at the Forward event in October 2024. UiPath is also expected to come up with a comprehensive agent orchestration platform with required security and agent ops
- Kore.ai: Kore.ai launched its platform named GALE to build, test, integrate and deploy AI agents and applications. The platform also comes with essential guardrails and analytics capabilities
With the slew of tech providers continuously entering this space, the market dynamics are bound to change. In the current landscape, our analysis (Exhibit 3) reveals four categories coming to the fore:
- Hyperscalers: hyperscalers are sizeable providers engaged in providing broader cloud, network, technology, and data services. Microsoft, Google, and AWS are the biggest names in this category, each with their own Agent frameworks, application programming interfaces (APIs) and even off the shelf agents in some cases. Hyperscalers have the financial clout and customer base to make significant advances and gain market share in Agentic AI
- Pureplay providers: pureplay providers operating in this field are mostly startups and AI native companies offering specialized capabilities for use cases, ranging from broad based to highly targeted ones. These players operate with an undivided focus on agentic AI and aim to continuously innovate in this category. Some notable names here are Ema, crew AI, Newo.ai, Relevance AI, Lyzr, Dust AI and so on
- Enterprise platforms: enterprise platforms are tech players that provide a centralized hub for a range of comprehensive software products/solutions such as customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP) and supply chain management (SCM). These are advanced software solutions that assist enterprises by integrating multiple functionalities into a cohesive system. As mentioned earlier, Salesforce and Service Now have already made announcements on their Agentic AI offerings on top of their existing platforms and others are now expected to follow suit
- Intelligent automation providers: these players are focused on streamlining business processes through a combination of rule-based automation and AI, using technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA), IDP, conversational AI, process orchestration and process intelligence. Some of these providers, such as Automation Anywhere, UiPath and Kore.ai have already launched their agentic platforms / capabilities, while others are on course to do the same in the near future
Apart from these tech providers, the ecosystem of tech services providers is also emerging where system integrators, managed services providers and consulting players are all expected to play a significant role in the agentic AI space through a range of advisory, solution development and operations services Exhibit 3: Emerging Agentic AI tech landscape Source: Everest Group (2024) 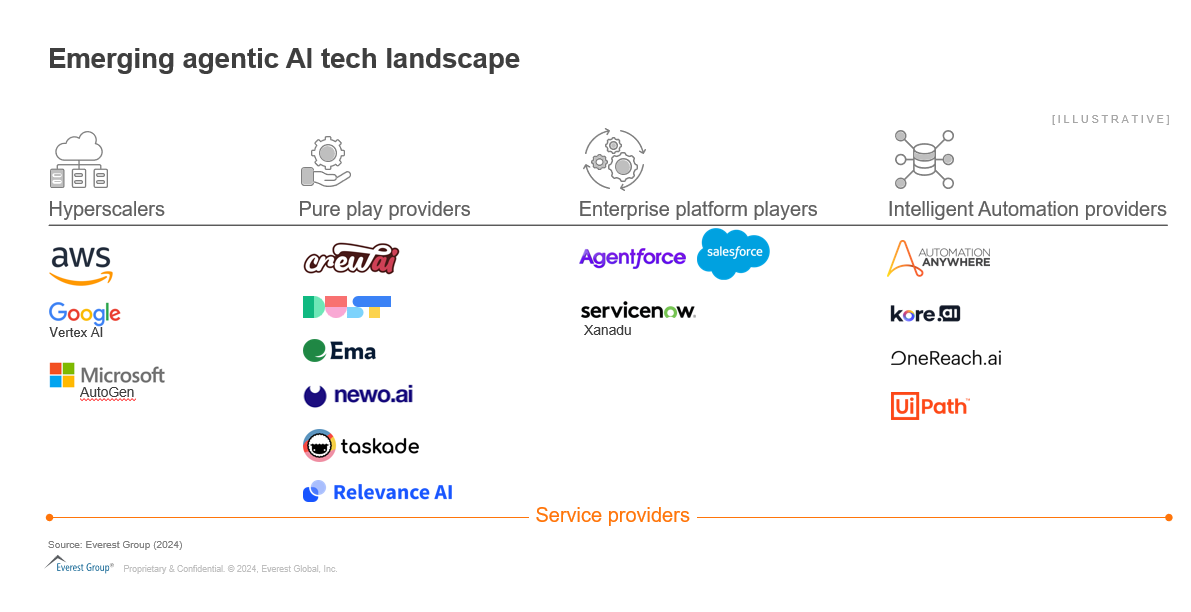 How should enterprises go about selecting the right tech partner for Agentic AI?
How should enterprises go about selecting the right tech partner for Agentic AI?
With the deluge of providers with diverse specialties operating in this space, the question being faced by enterprises is how to develop the right agentic AI ecosystem. Should they extend their relationships with their existing partners or explore new specialized partners focused on agentic AI? Identifying the right partner(s) begins with identifying what enterprises want to achieve in their agentic AI journey, and how the partner’s capabilities align with that vision. Here (Exhibit 4) is a framework that enterprises could use to evaluate their potential tech partner(s) for their agentic AI journey. Exhibit 4: Agentic AI tech provider evaluation framework Source: Everest Group (2024) 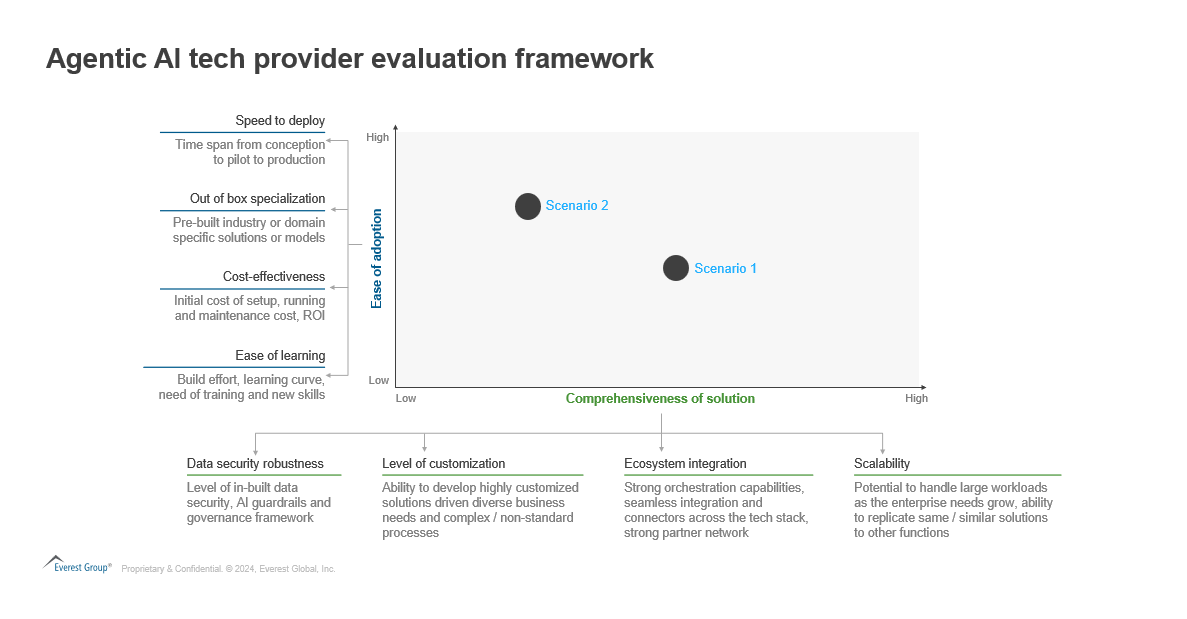 As a part of this framework, enterprises can evaluate providers across 2 dimensions, ease of adoption and comprehensiveness of solution. Ease of adoption is defined by the ability of the provider to deploy a fit for purpose solution at a fast pace with minimum disruption. On the other hand, comprehensiveness of solution covers the exhaustiveness, robustness and flexibility of the solution. The framework can be used by the enterprises to identify the category of the tech provider (as defined earlier in this blog) that will suit their needs and/or to evaluate and choose among multiple tech providers in one or more categories. Let’s consider a couple of scenarios to understand how enterprises can benefit from this framework.
As a part of this framework, enterprises can evaluate providers across 2 dimensions, ease of adoption and comprehensiveness of solution. Ease of adoption is defined by the ability of the provider to deploy a fit for purpose solution at a fast pace with minimum disruption. On the other hand, comprehensiveness of solution covers the exhaustiveness, robustness and flexibility of the solution. The framework can be used by the enterprises to identify the category of the tech provider (as defined earlier in this blog) that will suit their needs and/or to evaluate and choose among multiple tech providers in one or more categories. Let’s consider a couple of scenarios to understand how enterprises can benefit from this framework.
Scenario 1:
Situation: company A is one of the largest financial services companies in the world and deals with origination and servicing of personal and property loans. The company is required to process large amounts of data in a highly secure manner. It has already fostered a partnership with a hyperscaler for its data, cloud and AI needs. In recent times, the company has been seeing a decline in its business and there have been many unrecovered loans. The company aims to increase the loan volume as well as strengthen its loan disbursement mechanism to avoid losses. For this, it wishes to deploy an agentic AI system that reduces loan disbursement time and precisely identifies loan requests that are unlikely to be recovered. For this purpose, it is looking for an ideal tech provider that has the ability to deliver a scalable solution coupled with robust security measures. In the longer term, the company also plans to extend this solution to other standard as well as non-standard organizational processes.
Choosing the right partner: from the perspective of comprehensiveness of solution, company A is looking for an agentic AI provider with the capacity to deliver a solution with progressively increasing levels of complexity as the magnitude of the work increases. It should also exhibit robust security guardrails and ease of integration into the existing ecosystem. From an ease of adoption standpoint, an ideal partner would be a provider capable of rapid agentic AI development and deployment. In this case, it may make sense for company A to partner with a hyperscaler, preferably the existing partner, that can develop a robust customized agentic AI solution on top of the existing infrastructure and scale the solutions later as per organizational needs
Scenario 2:
Situation: company B is a small-scale logistics services provider operating a fleet of trucks for road-based transport. The company is not very mature in terms of leveraging automation except aspects of the business that are very standardized or repetitive in nature with little to no exceptions or dynamic situations. This means there is heavy reliance on manual workforce and dependence on their decision-making skills which is often not backed by sufficient data. Unanticipated weather conditions or political situations frequently require a proactive rerouting of shipments to ensure timely delivery. However, in the current scenario, this is more reactive, costing company B significant time and money. It wants to deploy an agentic AI solution that can reroute shipments on its own with minimal manual intervention. Given the cost associated with each route and rerouting, there is an urgent need to deploy a solution with minimum build and rollout time.
Choosing the right partner: as company B is a relatively small organization in the logistics market, it has limited resources available to invest in agentic AI. It is looking for a specialized solution with a low cost of investment. It should opt for a partner that is already servicing clients with its proven Agentic AI solutions and use cases in the logistics industry. In this case, it may make more sense for company B to partner with a pure play / niche agentic AI provider operating in the logistics space to launch a best-of-breed solution in a cost-effective manner. This will help it focus on its core competencies without big investments in the underlying solution development
Conclusion
While the agentic AI partner evaluation framework is a good aid, there is no one size that fits all approach that can be used in terms of partner selection. Ultimately, enterprises will have to make a choice between one or more players in the agentic AI tech landscape, keeping their needs, goals, and priorities in mind. For a big enterprise, a combination of multiple providers might work out as a better strategy, while for a small sized enterprise, being more focused might be a good strategy to begin with. Additionally, the agentic AI market is still very nascent and there are still a lot of unknowns.
As every provider comes up with their own set of agents and solutions, we are likely to see an agent sprawl. This will necessitate the need for proper orchestration, integration and governance mechanisms within the agentic AI solutions and ultimately these could become the deciding factor over everything else. With the number of start-ups burgeoning every day, we can also expect a significant consolidation in the months and years to come. Placing your bets on likely leaders and an ability to be agile can go a long way in emerging as a winner in the agentic AI journey!
If you found this blog interesting, check out our blog on Agentic AI – Exploring Its Enterprise Potential | Blog – Everest Group, which delves deeper into the topic of agentic AI.
If you have any questions, would like to gain expertise in artificial intelligence, or would like to reach out to discuss these topics in more depth, contact Vaibhav Bansal ([email protected]) or Vershita Srivastava ([email protected])