Blog
Decoding the Generative AI Buzz in Life Sciences

Advances in Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) have sparked interest in its potential to drive growth and innovation in the biopharma and medical devices industries. Despite challenges and regulations, the life sciences industry is actively exploring GAI’s possibilities. Learn about the current state of Generative AI adoption, the supplier landscape, and proactive actions stakeholders should take to stay at the forefront of this technology. Contact us
for questions or to have a discussion.
Life sciences, just like all other industries, is actively seeking to understand the intricacies of Generative AI (GAI) to gain a competitive edge. Enterprises in this industry are gearing up to embrace this generational shift in AI-enabled technology. Continue reading for the first part of our series on Generative AI adoption.
GAI is a type of machine learning that uses neural networks to learn patterns in the input data. Based on the input data it was trained on, GAI then generates the most appropriate response. GAI’s promise of delivering significant operational and tactical benefits in the short term and hyper-personalization and intelligent decision support over time is pushing life sciences enterprises to evaluate their Generative AI adoption readiness.
Although GAI can potentially disrupt the life sciences technology ecosystem in many significant ways, navigating the various risks and challenges that come with its implementation in this highly regulated industry will be critical.
Generative AI adoption outlook
Let’s take a look at the potential impact of GAI on the life sciences value chain:
- Building on the solid AI foundations in place, GAI is expected to have the greatest impact on the areas of drug discovery and research, and sales and marketing
- As organizations prioritize customer experience and new AI-based products emerge, the sales and marketing function is adopting GAI at a solid rate compared to the previous generation of AI applications
- Due to its huge potential across the development lifecycle – from novel design ideation to final prototyping – GAI is expected to impact medical device design and development, in addition to impacting R&D and commercial functions
- The biopharma and medical devices value chains have not yet fully embraced GAI because tools/GAI-based solutions trained on good quality LS-specific datasets are limited
The graphic below explores the short and long-term impact of GAI on various life sciences functions:
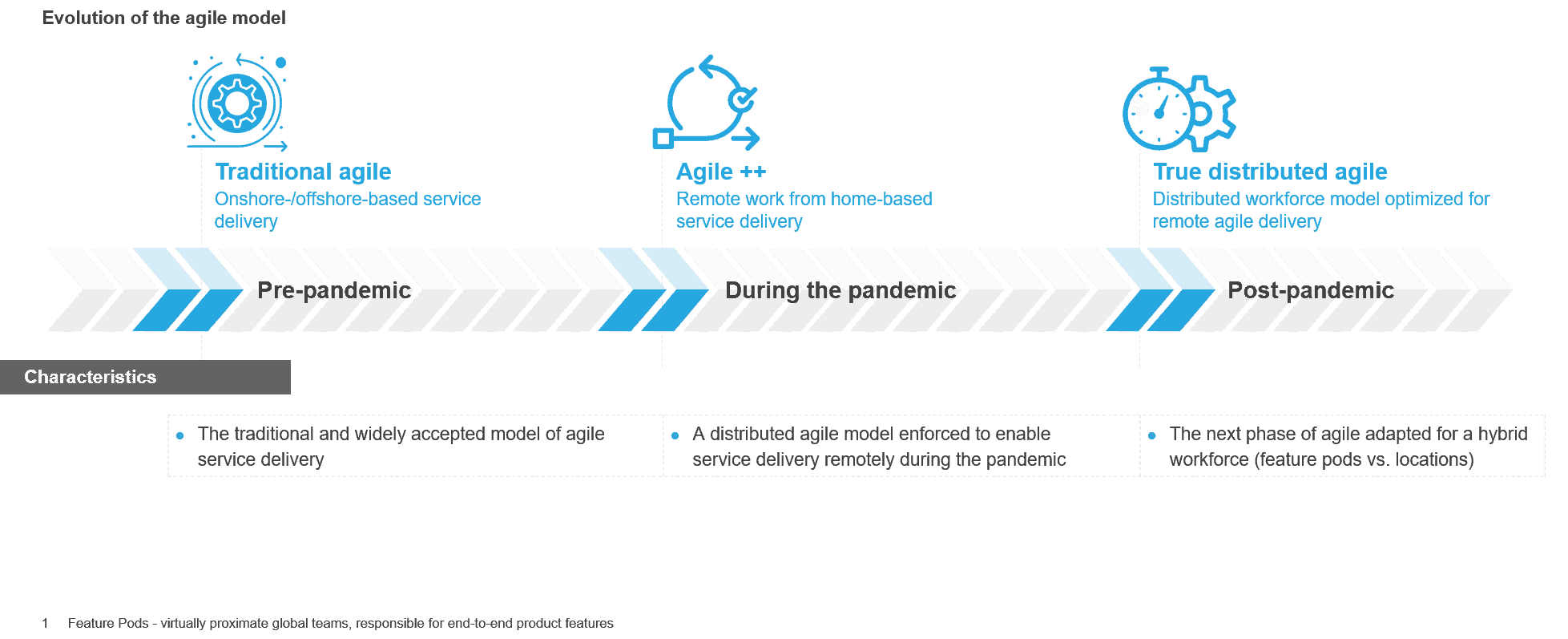
GAI can be used to model certain aspects of drug discovery. Some prominent cases include Insilico Medicine’s GAI platform Chemistry42 which generates ideas for novel chemical compounds, and AstraZeneca’s transformer-based model MegaMolBART for reaction prediction, molecular optimization, and de novo molecule creation.
As life sciences enterprises look to unlock GAI’s true value, its various stakeholders have exciting opportunities to collaborate and form next-generation partnerships to successfully drive GAI implementation. The supply ecosystem across the GAI technology stack is illustrated below:
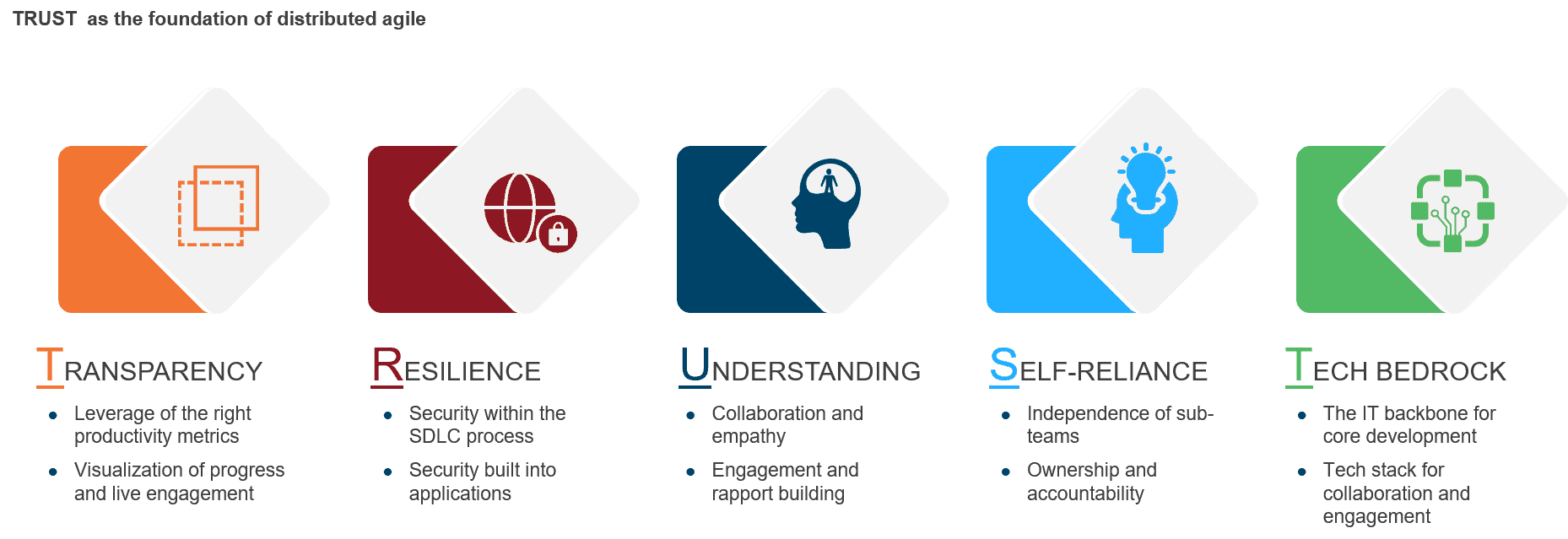
The following stakeholders have key roles in GAI’s future:
- Pharmaceutical and medical device enterprises: Enterprises such as Pfizer and Eli Lilly are partnering with independent software vendors to co-develop GAI solutions focused on enhanced efficiency, cost optimization, faster drug discovery, and remote patient monitoring while maintaining compliance with regulations
- Independent Software Vendors (ISVs): These firms offer highly specialized (pharma value chain element and/or technology-specific) productized GAI-enabled tools and have a wealth of domain expertise (cheminformatics, bioinformatics, genomics, etc.). Some players include Iktos, Yseop, and Huma.AI
- Hyperscalers: Cloud vendors have built AI/Machine Learning (ML)-specific modules for highly specialized functions such as omics analysis, high-performance computing (HPC) workload optimization, and knowledge graphs. Hyperscalers also offer a comprehensive suite of connectors and services to enable pharmaceutical companies to work with complex datasets
- IT service providers: Leveraging industry expertise and domain knowledge, these providers offer consulting services, training, and support. They also develop and deploy GAI solutions to pharmaceutical enterprises and ISVs
These stakeholder groups are uniquely positioned to act as catalysts for Generative AI adoption. The exhibit below looks at the actions each group should take to move forward with GAI and the implications:
Stay tuned for the second part of this blog series, where we will examine the most promising use cases in each area of the life sciences value chain, including their potential risks. We will also present a blueprint to successfully maximize the value of GAI-enabled solutions.
To discuss the future of Generative AI in life sciences, contact Kumar Dhwanit, or Rohit K.
Keep an eye out for our LinkedIn Live, The Possibilities for Generative AI in Sourcing.