Key Issues 2023: Assessing the Global Services Industry’s Performance Against Expectations | Blog
The global services industry’s confidence waned in 2023 after a banner post-pandemic year. Leaders were more cautious and prioritized cost optimization. To gain valuable insights into how the year unfolded compared to expectations, read on.
Participate in the Key Issues Survey 2024 to better understand the current thinking of industry leaders across the globe.
Coming off a bumper year in 2022 with double-digit growth driven by pent-up demand after the pandemic, the global services industry entered 2023 with macroeconomic uncertainty clouding the forecast.
As a result of these concerns, global leaders adopted a more cautious stance going into this year, according to Everest Group’s annual Key Issues survey of over 200 global leaders across industry enterprises, Global Business Services (GBS) centers, and providers.
In the survey, price and cost margin pressures ranked as the top business challenge expected in 2023, and subsequently, cost optimization emerged as the highest business priority for the year.
As 2023 nears an end and leaders start planning for 2024, let’s reflect on how the year fared against global services industry expectations of the industry.
1. Macroeconomic uncertainty subdued industry growth in 2023
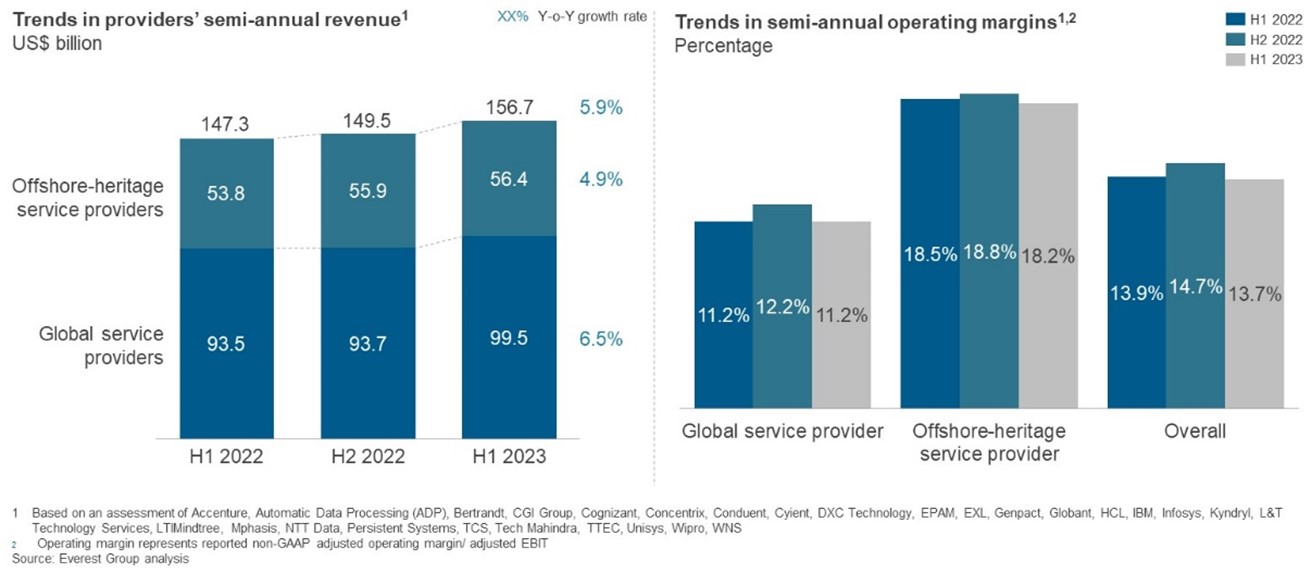
In the face of macroeconomic uncertainty, most industry leaders felt cautiously optimistic about 2023. True to their expectations, results from the first three quarters of this year indicate subdued industry growth similar to the pre-pandemic numbers. A mix of macroeconomic concerns, rising prices, fiscal tightening, and geo-political tensions have resulted in a slowdown in customer demand and growing margin pressures on the global services industry. While revenues grew, the escalated cost and price pressure resulted in stagnant or even declining operating margins for most providers, as presented in Exhibit 1.
Exhibit 1: Key financial metrics for providers for 2022-23
2. Talent demand and supply mismatch eased but remain challenging for niche skills
With attrition at an all-time high and growing industry demand, talent supply continued to fall short of the demand in 2022. The talent/skill shortage was the top concern industry leaders highlighted as part of the Key Issues Survey 2022. However, as the industry prepared for the looming uncertainty in 2023, these concerns took a back seat. In line with the industry expectations, the talent situation eased in 2023. Data for the first half of 2023 show that attrition rates have declined, and most delivery geographies are reporting a narrowing talent demand-supply gap. An assessment using Everest Group’s proprietary Talent GeniusTM tool indicates talent demand for delivery of IT and contact center services has declined substantially compared to 2022, as shown in Exhibit 2.
Exhibit 2. a: Talent demand across select countries for delivery of IT services indexed to January 2022 (Jan 2022 = 100)
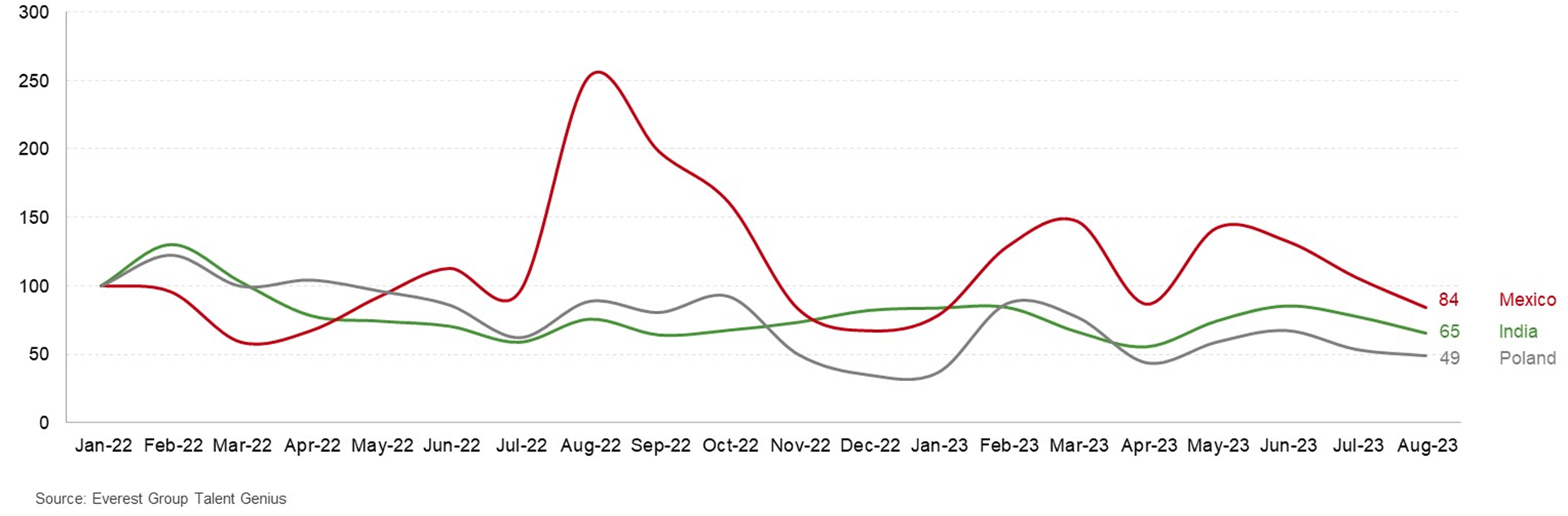
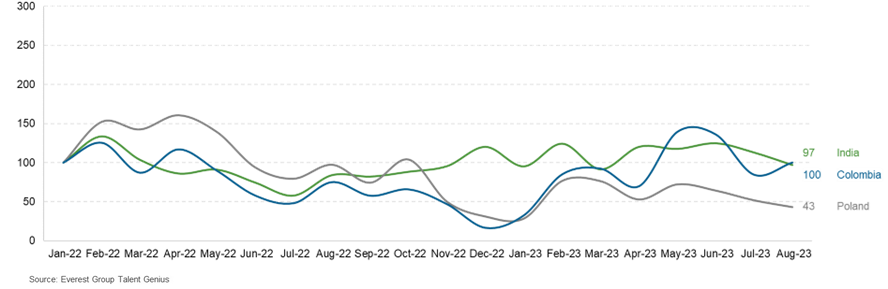
Exhibit 2. b: Talent demand across select countries for delivery of contact center services indexed to January 2022 (Jan 2022 = 100)
However, this improvement in talent supply has not applied to all global services, especially those requiring niche skills. Digital and next-generation technology services continue to witness a mismatch between talent demand and supply. This disparity is especially true for emerging skills like generative Artificial Intelligence (AI), where talent supply is even more limited. Preliminary estimates by Everest Group show that only 1% of AI talent has expertise in generative AI, pushing companies to focus on upskilling and reskilling their employed talent pools to bridge this gap.
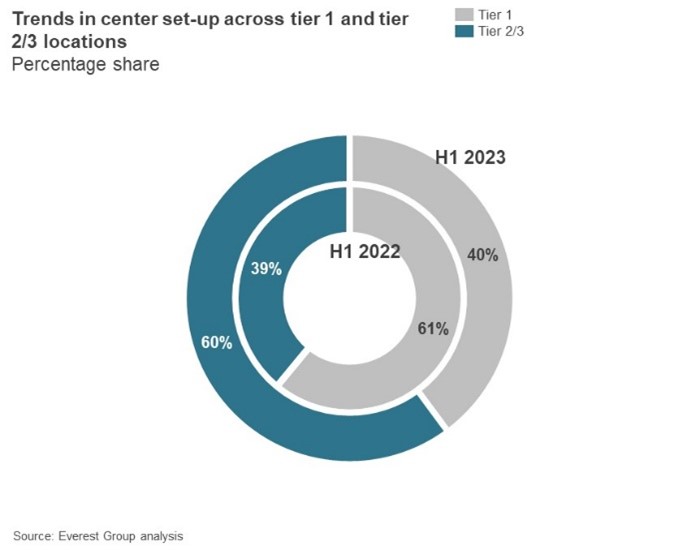
3. Offshore locations and tier 2/3 cities are being considered to optimize costs
To manage growing cost pressures, a key strategy for global leaders entering 2023 was continuing to leverage offshore locations and exploring alternative delivery strategies, such as leverage of tier 2/3 cities. Global services trends in 2023 resonate with this approach. Offshore locations like India continue to be the destination of choice for global service delivery, given the significant cost arbitrage opportunities. Similarly, enterprises and providers alike are more enthusiastically exploring tier 2/3 locations driven by needs of cost savings, talent access, employee preference, and market competition management. Exhibit 3 shows how the leverage of tier 2/3 cities witnessed growth in 2023.
Exhibit 3: Trends in center setup across Tier 1 and Tier 2/3 locations (2022-23)
4. Provider bill rates increased but at lower levels than expected
Despite the prevailing macroeconomic pressures, providers maintained optimism about bill rate increases in 2023, although they were expected to be at a lower rate than in 2022. Unlike other economic downturns, provider bill rates have continued to show positive growth despite the growing cost and price pressures in the first seven months of 2023. However, with the macroeconomic scenario hitting much harder than expected, input-based pricing has been subjected to hard negotiations. This has led to muted growth (0.5-2%) in bill rates across different functions, much lower than provider industry expectations going into 2023. For example, provider bill rates for traditional applications skill delivery in offshore regions grew by only 0.5-1% compared to the expected growth of 2-5% from January to July 2023.
5. Provider portfolios underwent significant rebalancing and consolidation to ensure better deal terms
Enterprises reported much lower satisfaction with providers in 2022 compared to 2021 when providers played a key role in supporting enterprises in navigating the pandemic. The leaders cited a lack of innovation and communication as the key reasons behind this dissatisfaction. Consequently, procurement leaders expected a significant change in their provider portfolios. Additionally, with macroeconomic concerns clouding all strategies, enterprises looked to consolidate and rebalance provider portfolios to negotiate better deal terms with limited providers. As expected, 2023 witnessed a shift in provider portfolios, with major providers winning deals that had vendor consolidation components.
6. Investments in strengthening the digital core are a priority over moonshot endeavors
Prioritizing resilience through uncertainty, the focus of the global services industry continues to be on pragmatic digital investments like cloud solutions, cyber security, analytics, and automation. While the advent of newer technologies like generative AI has created an industry buzz, the primary focus continues to be on strengthening the digital core and building a resilient technological foundation. Most industry verticals continue to wait and watch before diverting constrained resources to newer projects with limited use cases and industry adoption.
As 2023 comes to a wrap, the global services industry is at the forefront of another transformative shift – the need to create value and the need to create it fast. This becomes especially imperative as technological advancements like generative AI threaten to shift the industry’s current equilibrium and potentially start the next phase of a technological revolution. The global services industry must adapt swiftly to stay ahead of the curve.
Participate in our Key Issues Survey 2024 to capture the pulse of Information Technology and Business Processing industry leaders across the globe and uncover major concerns, expectations, and key global services trends that are likely to amplify in 2024. To discuss further, or for any questions, reach out to Ravneet Kaur or Hrishi Raj Agarwalla.
Don’t miss the Key Issues 2024: Creating Accelerated Value in a Dynamic World webinar to gain valuable insights into 2024.