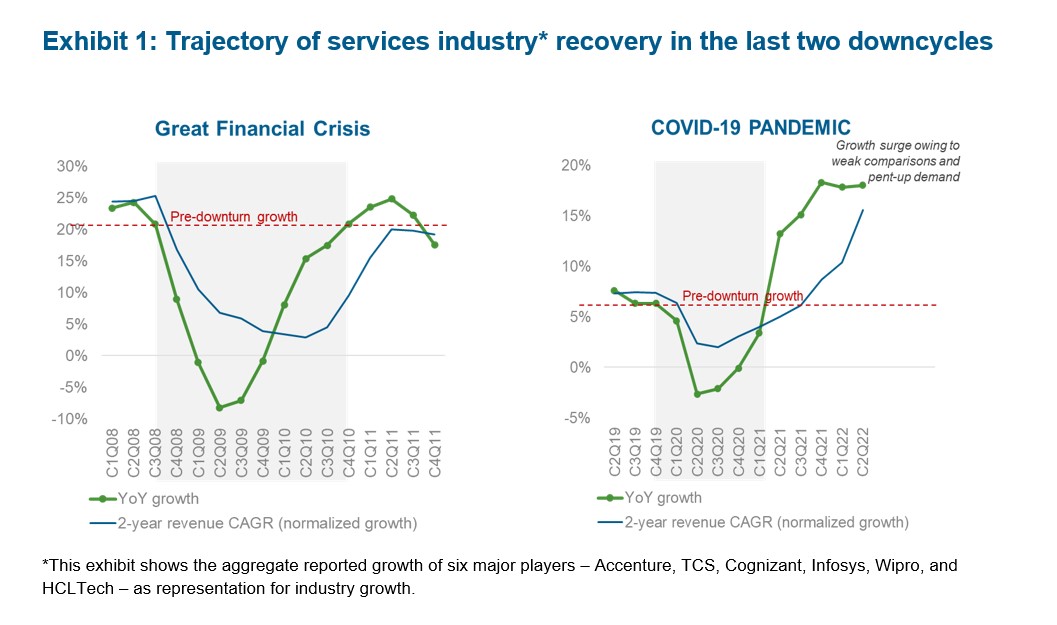
April 3, 2024
Post-quantum cryptography (PQC) has become essential for enterprises to protect against future quantum-enabled attacks and secure digital assets and sensitive data. Read on to discover providers’ crucial role in preparing enterprises for PQC. Reach out to explore this topic further.
As discussed in our previous blog, the emergence of quantum computing poses a significant threat to current public key cryptographic methods. When run on quantum computers – or more specifically, Cryptographically Relevant Quantum Computers (CRQCs) – some algorithms such as Shor’s can potentially break widely used methods like RSA, DSA, ECDSA, EdDSA, and DHKE, among others.
The advancement of quantum computers can seriously threaten data security and privacy for various enterprises, affecting fundamental principles such as confidentiality, integrity, and authentication. This makes it essential to reassess the security of these cryptographic methods.
The early and widespread use of quantum computers could wreak havoc, enabling new advanced cyberattacks that are impossible using classical computers. Post-quantum cryptography (PQC) is the solution to this problem. Let’s explore this further.
What is post-quantum cryptography?
In the quantum computing era, PQC is vital in ensuring the long-term security of digital communication and data protection. PQC focuses on researching and adopting cryptographic algorithms that are ready for this era.
These algorithms are designed to be secure against both quantum and classical computers. Furthermore, they are expected to be deployable and integrable without significant modifications to current protocols and networks.
With extensive ongoing research in this field, researchers have proposed several mathematical schemes that meet the requirements for being potential candidates for quantum-safe cryptographic algorithms. These include lattice-based, multivariate polynomial, code-based, hash-based, and isogeny-based cryptography.
The U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) launched a program in 2016 to create standardized quantum-safe cryptographic algorithms.
After a rigorous six-year evaluation involving global experts, it announced four finalists for quantum-safe cryptographic standards. The following algorithms selected by NIST address general encryption and digital signatures that are crucial for securing data exchanges and identity authentication:
| PQC algorithm |
Cryptographic scheme |
Purpose |
| CRYSTALS-Kyber |
Lattice-based cryptography |
Key encapsulation method (KEM) |
| CRYSTALS-Dilithium |
Lattice-based cryptography |
Digital signature |
| FALCON |
Lattice-based cryptography |
Small digital signature |
| SPHINCS+ |
Hash-based cryptography |
Digital signature |
Several other developments related to PQC have occurred recently. The notable ones are highlighted below:
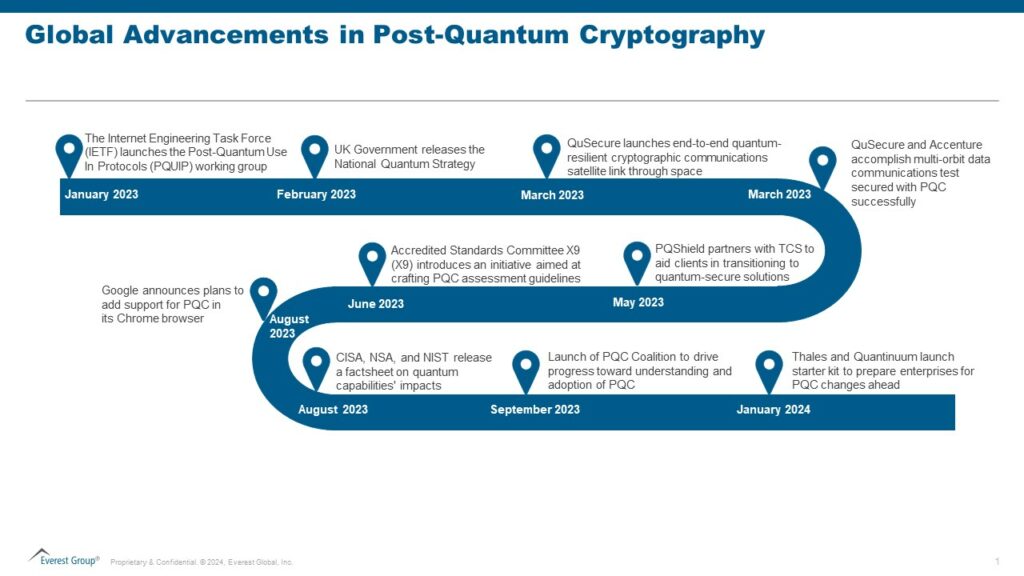
Common cryptographic pitfalls
The complexity of cryptographic fields makes it difficult for enterprises to navigate data security. With numerous algorithms, protocols, and standards, enterprises often struggle to understand and implement robust cryptographic solutions.
Enterprises may encounter several common cryptographic pitfalls, including:
- Lack of awareness about cryptographic algorithms used for data protection
- Dependency on long-life data secured by cryptographic schemes not suitable for the quantum computing era
- High costs and efforts required to update cryptography across systems and applications manually
- Use of outdated cryptographic algorithms
- Challenges in ensuring interoperability between different cryptographic systems and protocols, especially in hybrid IT environments
- Limited resources, including security budget and expertise, hindering effective cryptography implementation and management
- Risk of vulnerabilities and security breaches due to incorrect implementation of cryptographic protocols or algorithms
Enterprise considerations for embracing PQC
Considering the current challenges with cryptography, enterprises would face far more significant difficulties if they do not strategically plan for PQC. To prevent this, cybersecurity leaders globally must proactively prepare and initiate early plans to migrate to post-quantum cryptographic standards.
Taking a proactive stance is crucial since transitioning to new quantum-safe algorithms will be discontinuous, considering the inherent disparities in key size, error-handling properties, and other complexities.
Hence, enterprises should give themselves enough time to start small, experiment, learn from positive impacts and challenges, and explore ways to reduce technology transition costs.
Steps to establishing a quantum readiness roadmap
Staying abreast of advancements in quantum computing and quantum-safe solutions is paramount. Enterprises must establish a comprehensive quantum readiness roadmap following these five steps:
- Inventory quantum-vulnerable systems: To kickstart readiness efforts, enterprises should conduct a thorough inventory of quantum-vulnerable systems across both information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT) environments, covering all cryptographic assets, including keys, certificates, protocols, libraries, and algorithms. Understanding cryptographic assets and algorithms, locations, and purposes is a fundamental best practice, especially when preparing for post-quantum cryptography. It is also crucial to identify where long-life data resides, comprehend data flows, and understand the types of cryptography used to protect it.
- Conduct an internal risk assessment: This can help identify and prioritize assets most impacted by a quantum computer cryptographically, thus exposing the organization to greater risk. Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and Chief Revenue Officers (CROs) must ensure that quantum risk mitigation is integrated into existing risk management strategies.
- Engage with technology vendors: Partner with supply chain providers to understand their quantum readiness roadmaps and migration strategies to facilitate a smooth transition that aligns with enterprise goals and timelines.
Streamline the current cryptographic infrastructure: Enterprises can initiate modernization efforts by streamlining their current cryptographic infrastructure, including consolidating or replacing vendors to enable a managed migration process. The CFO should collaborate with other executives to prioritize PQC investments based on the risk appetite and strategic objectives and adopt a fully crypto-agile approach. Establishing a governance structure with clearly defined roles and responsibilities to adopt PQC effectively is also recommended.
- Adopt PQC algorithms: Enterprises eventually should integrate PQC algorithms into browsers, applications, public key infrastructure (PKI), files, and data systems, wherever quantum-vulnerable cryptography is employed. CIOs must collaborate closely with CISOs and other stakeholders to assess the compatibility of current systems with PQC solutions.
There is an ongoing debate over some adversaries already gathering encrypted foreign communications, anticipating the future ability of quantum computers to decrypt such systems, and aiming to extract valuable secrets from the data collected. This threat, known as “harvest now, decrypt later,” highlights the urgency of making cryptographic changes rather than waiting.
How can service providers help enterprises navigate the PQC era effectively and efficiently?
As quantum computing advances, the demand for comprehensive quantum-resistant cryptographic solutions will only increase, favoring a ripe market for cybersecurity service providers to capitalize on.
PQC offers a significant opportunity for providers to position themselves as vital partners in ensuring the security and resilience of enterprises’ digital assets against the evolving quantum computing threats.
Leaders may need help understanding the advanced mathematical concepts and algorithms involved in PQC. The complexity of these cryptographic methods may need to be clarified for enterprises trying to grasp the intricacies of quantum-resistant solutions.
With all the latest discussions about quantum computers, service providers should take this time to develop a perspective on how PQC would impact enterprises from various industry verticals.
Providers should play an educational role, creating awareness about the risks posed by quantum computing and guiding enterprises on the importance of proactively transitioning to quantum-resistant solutions.
Service providers should develop strategies to hire, train, and upskill talent in PQC and quantum computing concepts. Additionally, they can invest in R&D initiatives to explore new approaches and solutions in the PQC field. By collaborating with relevant technology vendors, research institutions, and other organizations paving the way for PQC, service providers can foster innovation and help their clients stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
Cybersecurity service providers can offer specialized consultation and assessment services to help enterprises evaluate and inventory their current cryptographic infrastructure, prioritize components based on risk, identify vulnerabilities to quantum attacks, and recommend appropriate post-quantum cryptographic solutions.
Moreover, they can engage with enterprises on initial levels to develop comprehensive strategies for implementing and managing these solutions effectively, ensuring seamless integration with existing security frameworks and compatibility with legacy systems.
Unlocking potential: Exploring use cases with PQC
Service providers should prioritize PQC to address the threat quantum computing poses to traditional cryptographic systems. By embracing PQC, service providers can safeguard their clients’ data and infrastructure against potential quantum attacks.
Additionally, they can explore new use cases for PQC to unlock innovative solutions and stay ahead of the curve in the rapidly evolving quantum landscape. These new use cases may include:
- Quantum-safe communication (use cases for cloud computing, data centers, 5G networks, secure private communication links, )
- Security in the banking sector, securing ATM and online credit card transactions, as well as customer data stored in bank data centers
- Quantum-safe VPN and SD-WAN
- Quantum-safe cybersecurity for automotive systems
- PQC in Internet of Things (IoT) and Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) domains for protection of data transmitted between connected devices and central data processor/edge servers
- Quantum-safe blockchain
- Safeguarding the storage, transmission, and processing of sensitive patient data in healthcare (including that collected by biosensors in wearable devices)
- Quantum-safe PKI for OT environments
- PQC in Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
Envisioning the future
PQC is no longer a theoretical concept but a reality. Multiple applications of PQC have emerged. In their latest release, OpenSSL has fully enabled PQC for digital signatures and fundamental establishment mechanisms. The Signal Protocol, an essential constituent of Signal, Google RCS, and WhatsApp messengers, has also announced support for the PQXDH protocol, becoming the first to introduce PQC for the initial key establishment. Apple has introduced a fresh encryption protocol named PQ3 for iMessage, offering advanced post-quantum security measures for instant messaging.
PQC is rapidly gaining traction for quantum-safe digital signatures, encryption, and fundamental exchange mechanisms. Its widespread adoption seems inevitable as the risks of quantum supremacy proliferate.
The standardized algorithms aren’t battle-tested yet, and exploitable weaknesses could be uncovered, leading to adjustments in their functioning or the development of entirely new algorithms.
We anticipate PQC becoming the cornerstone of cybersecurity strategies in the coming years. Moreover, the security standards are expected to recommend or mandate PQC.
PQC has become a crucial element of enterprise security, safeguarding against quantum-enabled attacks and ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive data.
Enterprises must start planning to migrate from a secure lock to an unbreakable vault: post-quantum cryptography! Service providers play a crucial role in guiding and supporting enterprises every step of the way.
To discuss post-quantum cryptography further, please contact Prabhjyot Kaur, Kumar Avijit, and Ronak Doshi.