Beyond the Hype: Approaching Gen AI in BFSI Enterprises with the Generative AI-EXCEL Framework | Blog
To successfully adopt Gen AI in BFSI, enterprises need to consider four fundamental aspects that can lead to responsible and effective deployment. Carefully evaluating each framework component is essential to ensure a positive Gen AI journey. Read on to learn about the Generative AI-EXCEL Framework and the importance of each element, or get in touch.
As there is urgency to embrace Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI) across all industries – the BFSI industry is no exception given its prevalence. However, a thoughtful approach is required to fully reap the benefits of Gen AI.
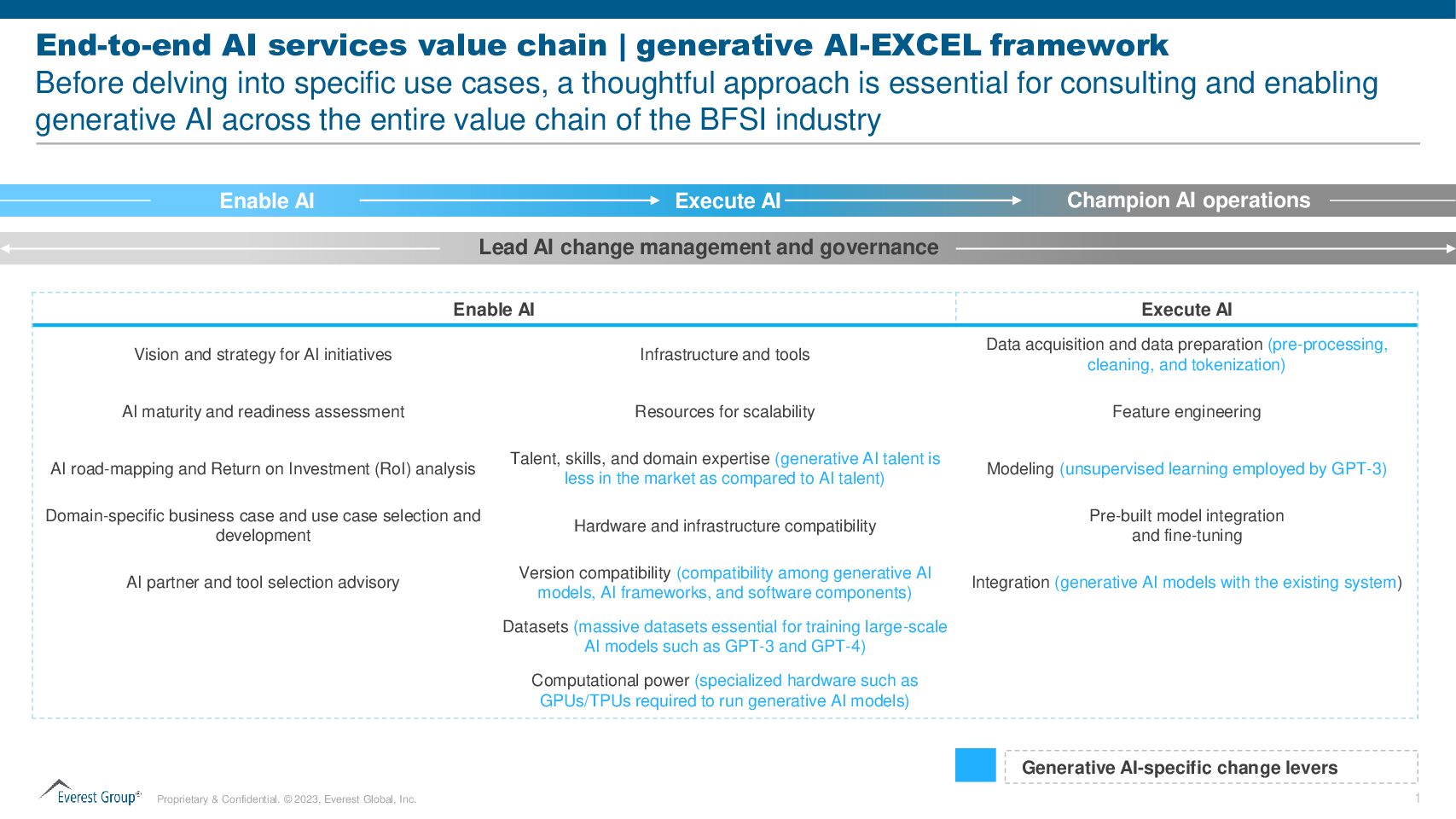
Before immersing themselves in various use cases and integrating Gen AI into their operating structure, BFSI enterprises should strategically examine four fundamental components along the Gen AI value chain:
Generative AI-EXCEL framework
- Enable AI
- Execute AI
- Champion AI Operations
- Lead AI Change Management and Governance
These elements can guide enterprises toward harnessing the full potential of Gen AI in BFSI while ensuring responsible and effective deployment.
Enable AI
Embarking on AI initiatives demands the expertise of AI experts to define a clear vision and strategy. Seeking guidance from Gen AI experts is essential in laying a solid foundation for successful implementation. Assessing organizational readiness through an AI maturity and readiness assessment is recommended as this can provide insights into preparedness levels and potential challenges.
Developing a Gen AI roadmap and conducting a Return on Investment (ROI) analysis further ensures a well-structured approach, allowing organizations to navigate the complexities of integrating Gen AI effectively in their operations. A thoughtful approach is essential for consulting and enabling generative AI across the value chain before delving into specific use cases, relying on AI technology partners, and tool selection advisory services to ensure that organizations secure the right resources for success.
Adequate resources are crucial to ensure scalability, allowing Gen AI systems to manage increasing workloads efficiently. There is a lot of demand for talent, skills, and domain expertise, especially in Gen AI that needs to be plugged.
Moreover, hardware and infrastructure compatibility and version compatibility among different Gen AI models and frameworks are essential for seamless operations. Massive datasets play a pivotal role in training large-scale AI models, demanding significant computational power from specialized hardware such as graphics processing units (GPUs) and tensor processing units (TPUs). Balancing these elements is vital to harness the potential of Generative AI effectively.
Execute AI
When developing AI systems, some essential steps include preparing the data, refining features, utilizing and fine-tuning pre-built models, integrating AI with existing systems, creating custom models as needed, and conducting thorough testing to ensure reliability.
The increasing complexity of Gen AI models has led to the emergence of Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) and Large Language Model Operations (LLMOps) as services. These can play a pivotal role in easing the efficient deployment, orchestration, and monitoring of AI models.
Given the possibility of potential biases introduced by Gen AI, it becomes imperative for BFSI enterprises to ensure fairness. Vigilant model monitoring and drift analysis are some ways to achieve this. In addition, optimized performance can be achieved by incorporating accelerators.
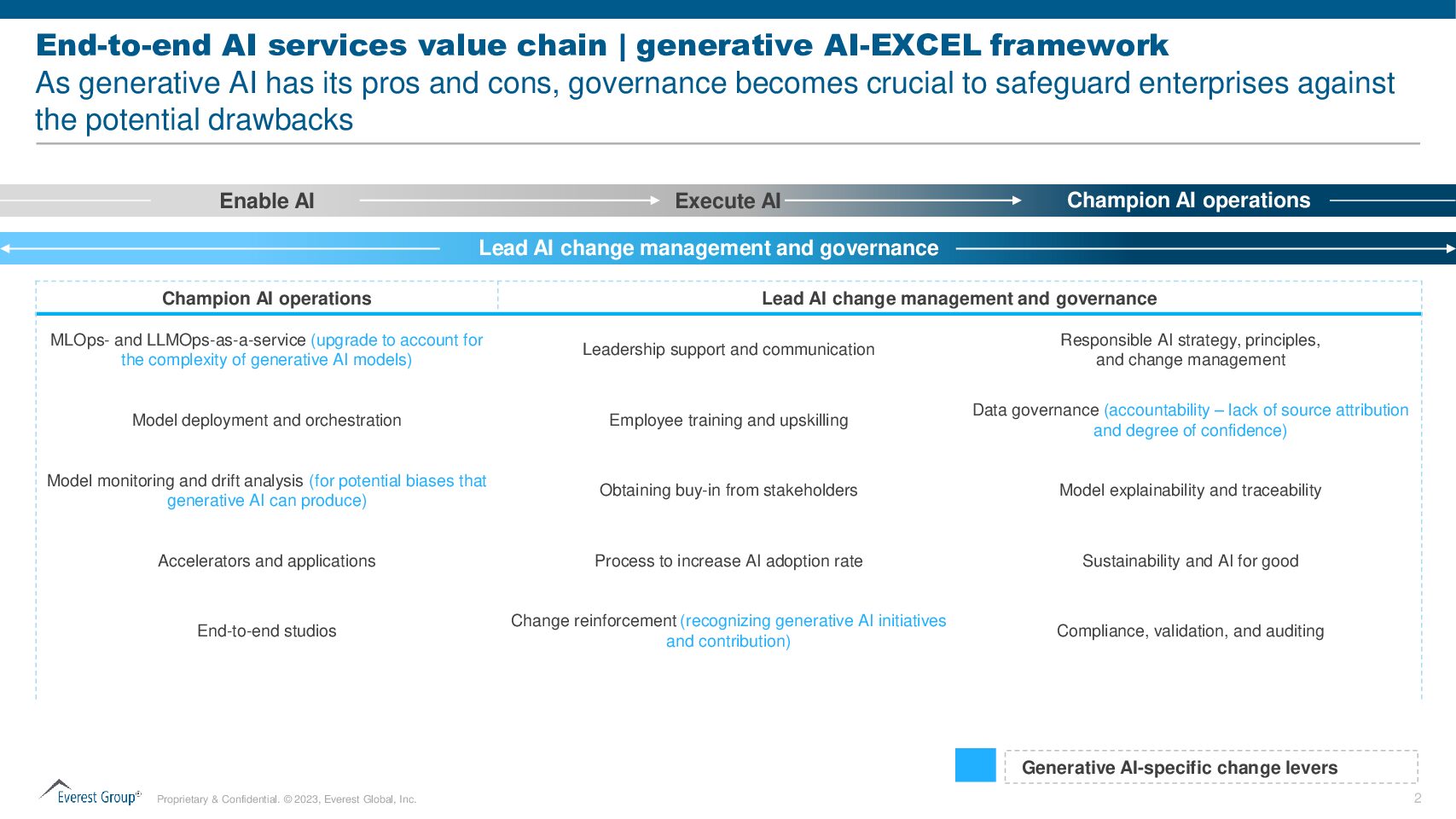
Champion AI Operations
A robust change management strategy is essential for navigating a smooth transition. Leadership communication about AI’s benefits can set a positive tone for adoption. Equipping workforce with the necessary skills through comprehensive training and upskilling is essential. Developing a streamlined process for Gen AI adoption can enhance its acceptance rate. Recognizing and reinforcing Gen AI’s contributions can motivate the workforce, ensuring effective and sustainable AI integration.
Lead AI Change Management and Governance
Strong data governance can help address some of the concerns related to source attribution and confidence levels in data and foster trust in Gen AI outcomes.
Gen AI can generate content that is low in authenticity. Model explainability can help make AI decisions more understandable and traceable, boosting user confidence. Furthermore, enforcing compliance, validation, and auditing mechanisms can reinforce AI solutions’ reliability and ethical deployment.
The Gen AI model can potentially produce biased or dangerous results. Other AI models can be used to test results for risky outputs. Enterprises can also use data loss prevention and other security tools to prevent users from inputting sensitive data into prompts in the first place. Maintaining control over data is essential, and multiple levels of security are required.
In an industry where data security and privacy are paramount, governance becomes a linchpin for safeguarding sensitive information. Beyond regulatory compliance, governance can address critical aspects such as risk management, fairness, transparency, and accountability. With ongoing regulatory uncertainty and evolving laws, it is critically important to exercise caution about data breaches, privacy violations, or biased or discriminatory decisions that can create regulatory liabilities.
By following this Generative AI-EXCEL framework, BFSI enterprises can ensure they have addressed all essential aspects of enabling Gen AI. From identifying the right infrastructure and resources to developing and testing models and ensuring proper change management and governance, thoroughly evaluating each component guarantees a smooth AI transition. This approach will allow BFSI enterprises to harness Gen AI’s power fully.
To discuss Gen AI in BFSI, please reach out to [email protected], [email protected], and [email protected]. Learn more about how we can help your enterprise to leverage Gen AI, or read our report on revolutionizing BFSI workflows with Gen AI.