Transforming the Game: How Consolidation is Revolutionizing the Insurance Brokerage Industry | Blog
Readily available capital and low-interest rates made the past few years ideal for the insurance brokerage industry to consolidate in response to increased competition, changing customer expectations, and other challenges. Merged insurance intermediaries can partner with business process service (BPS) providers to optimize processes, manage risks, enhance data analytics, and improve customer experience, among other benefits. Read on to learn more.
Reach out to us directly for questions or to learn more.
The insurance brokerage industry went through an inflection point last year. A confluence of factors happening simultaneously created a perfect recipe for consolidation. These included large quantities of readily available capital, low-interest rates, highly valued broker stocks, all-time high valuation multiples, and the challenging insurance market.
The deal frenzy of 2021 slowed towards the end of 2022, with less than $2 billion of deal value announced and no large transactions in the last six months of the year. Despite this, insurance brokerage transactions trumped the activity. More than 90% of the overall insurance deals were in the brokerage space. In terms of both the volume of transactions and the multiples being paid, the consolidation rate in the re/insurance broker industry has accelerated.
Let’s take a look at the following dominant broker groups influencing the insurance brokerage industry:
- Global brokers – Large multinational insurance brokers who typically operate in multiple countries and offer a wide range of insurance products and services
- Private Equity (PE)-backed brokers – PE firms provide the necessary capital for mergers and acquisitions
- Family-owned brokers – Small to mid-sized insurance brokers that are family owned and operated
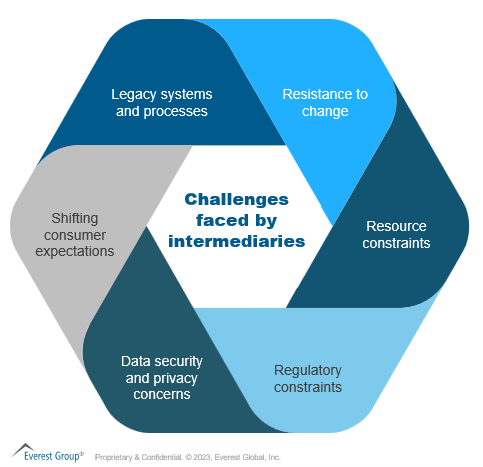
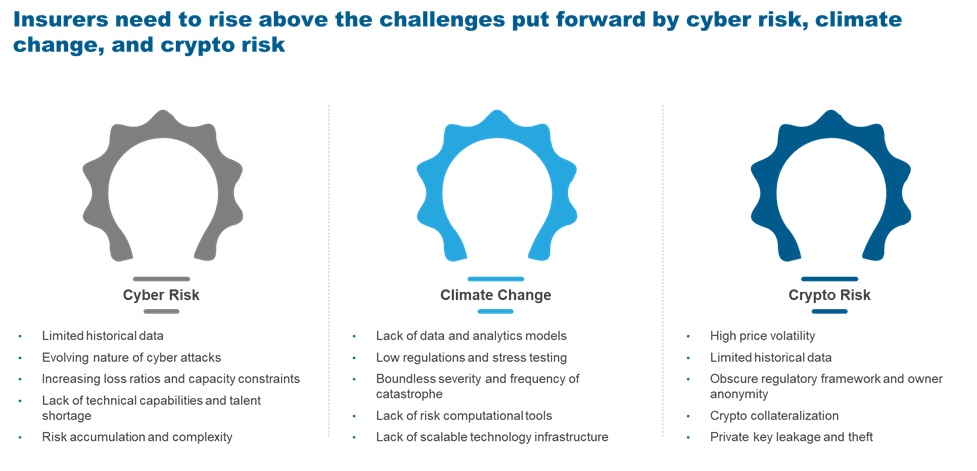
Drivers and challenges leading to consolidation
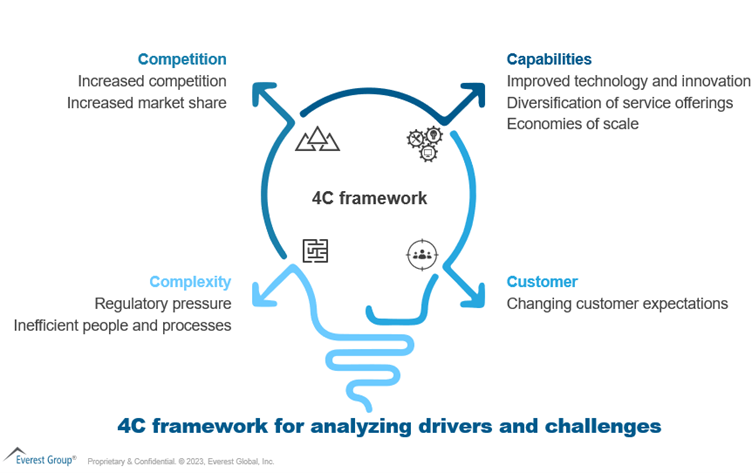
Competition
- Increasing competition: The insurance intermediary industry is becoming increasingly crowded, with new players entering it all the time, further fragmenting the market. These new players often can offer better services, lower prices, and more innovative solutions than traditional insurance intermediaries
- Market share growth: Insurance intermediaries can inorganically boost market share with additional capabilities and market penetration in new geographies by consolidating with another firm. They also can benefit from customer base growth
Capabilities
- Technological advancements: The industry’s recent drive towards digital transformation by implementing new technology and platforms is forcing intermediaries to seek funds to invest in digitization or lose against better-capitalized intermediaries
- Economies of scale: Insurance intermediary consolidation can spread fixed costs over a larger number of policies, resulting in lower average costs per policy. It also can provide intermediaries with increased bargaining power with insurers, provide cross-selling and up-selling opportunities, and help increase brand and mind share
- Service offering diversification: Consolidation allows insurance intermediaries to expand and diversify their services and product lines. Intermediaries can attract new customers by acquiring another brokerage that provides different products or services. This keeps intermediaries relevant and competitive in a dynamic market
Complexity
- Regulatory pressure: Consolidation can help smaller intermediaries remain up to date on increasingly complex risk management requirements that would be difficult for them to do by themselves
- Inefficient processes and people: By joining forces, smaller firms can improve process efficiencies and combine their talent pools. Consolidation also can help large entities better manage operations
Customer
- Changing customer expectations: Consumers increasingly demand customized and convenient services and anticipate an omnichannel experience. Insurance intermediaries that cannot meet shifting consumer expectations risk losing clients to rivals who can.
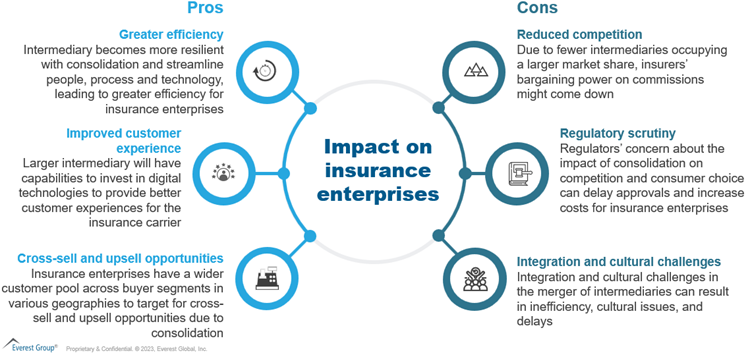
Impact of consolidation on stakeholders
Insurers
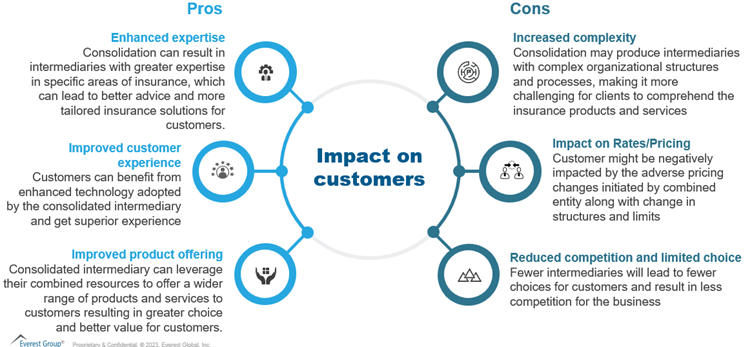
Customers
Routes to consolidation
Insurance intermediaries can take multiple paths to consolidate depending on their strategy, such as:
- Mergers & Acquisitions: This is the preferred route for consolidation where two or more intermediaries enter into an M&A to achieve economies of scale, expand into new markets, and gain access to the latest tools and technologies. Different forms of M&A pursued are horizontal mergers between intermediaries from the same market, vertical mergers between intermediaries with different capabilities, and cross-border M&A
- Strategic alliances and joint ventures: Insurance intermediaries can pursue strategic alliances or JVs under many forms, such as distribution agreements, co-marketing agreements, and shared service agreements to effectively share resources and expertise while reducing risks and increasing market power
- PE investments: In recent years, PE firms have increased their involvement in this industry as they look to invest in dependable, cash-generating companies with room for expansion. PE companies can assist insurance intermediaries seeking strategic acquisitions and expansions while also providing access to finance and experience
Many intermediaries also take an independent route and pursue organic growth by investing in digital transformation initiatives to achieve unparalleled scale and efficiency.
Key players in the insurance intermediary consolidation space
The insurance intermediary market is highly competitive and dynamic, with many players pursuing different strategies to achieve their growth objectives. Here are some of the active players in the consolidation space:
- Marsh & McLennan: In 2019, the company acquired Jardine Lloyd Thompson Group, a leading UK-based insurance intermediary, in a deal valued at $5.6 billion. The company also has announced the acquisition of Focus Insurance, offering tailored personal insurance programs.
- Gallagher: Gallagher has pursued a growth strategy focused on M&A and has completed over 500 acquisitions since 1984. Gallagher started 2023 with an acquisition of Dublin-based commercial and personal lines broker First Ireland, making it one of Ireland’s largest brokers.
- Hub International: The company also is focused on growth through M&As, and has made more than 600 acquisitions since its founding in 1998. In 2020, Hub acquired the assets of The Insurance Exchange, Inc., a leading insurance brokerage firm in California.
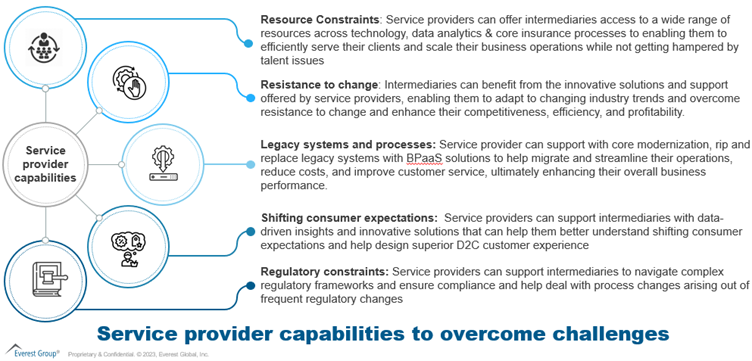
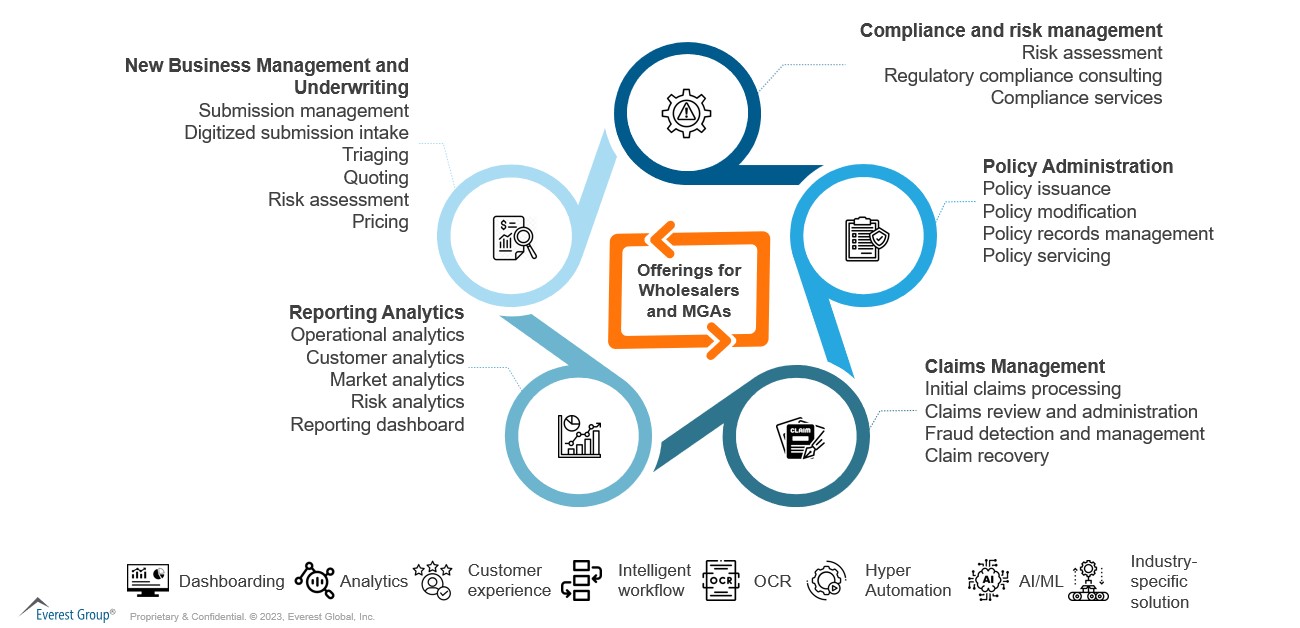
How intermediaries can leverage insurance service providers
Intermediaries face increasing pressure to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and deliver better customer experiences. By partnering with BPS providers, they can achieve these goals. BPS providers can deliver policy administration, claims processing, customer service, data analytics, and other services, as illustrated below:
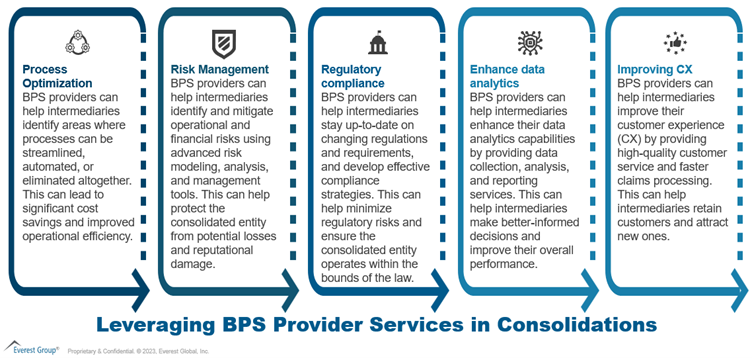
In selecting a BPS provider, intermediaries need to evaluate the service provider’s capabilities by carefully considering their expertise, experience, cost arbitrage, flexibility, security, business continuity, delivery footprint, talent maturity, technology, infrastructure, governance approach, and client-centricity.
Everest Group can help evaluate these capabilities through its proprietary PEAK Matrix® assessment and impartially rank service providers as leaders, major contenders, and aspirants, as well as provide expert commentary to help enterprises make better-informed decisions.
To discuss insurance brokerage industry trends, please reach out to [email protected] and [email protected], and stay updated by accessing Everest Group’s latest research on Insurance Business Processes.