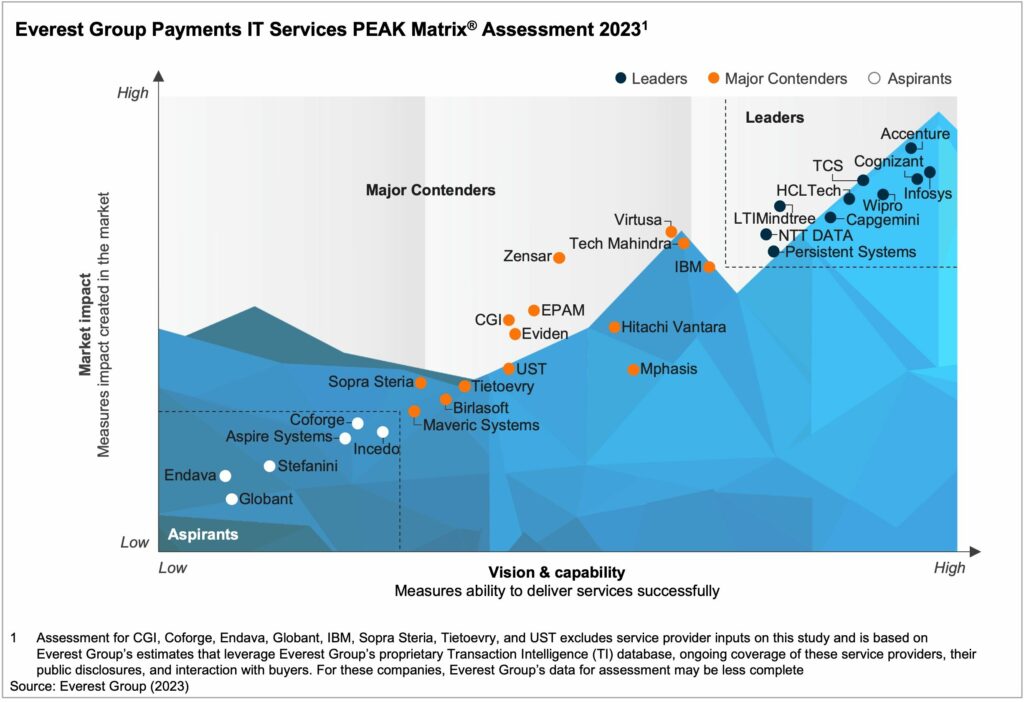
Unlocking Enterprise Preparedness for T+1 Settlement: The Crucial Role of IT and Technology Services Providers | Blog
By partnering with IT and technology services providers, banks and financial institutions can prepare for the new T+1 settlement. This security trade rule change to shorten the order finalization date by a day is expected to enhance operational efficiencies and reduce risk. Read on to understand how this updated regulation will impact the industry landscape and rapidly transform critical areas. Reach out to discuss the topic with us.
In today’s ever-evolving financial industry, the shift to T+1 settlement aims to enhance market efficiency, reduce counterparty risk, and align North American markets with global standards.
The transition to a T+1 settlement cycle represents a monumental shift for banks and financial institutions that will impact trade management, resource allocation, and risk mitigation.
Scheduled to go into effect this May in the US and Canada, the amended rule would require trades to be settled just one day after the transaction date, marking a significant departure from the current two-day cycle.
Let’s explore its ramifications further.
Impact on investors
Shifting toward instantaneous or faster settlements is a remarkable milestone that will streamline operations, improve risk management, boost liquidity, and provide better counterparty risk management. This will further lead broker-dealers to reduce margins and collateral requirements.
Accelerating settlement cycles will save buyers and sellers time and increase trading volume. The positive impact will vary by the investor type. Large institutional investors like corporations will benefit from more liquidity and reduced margin requirements. Meanwhile, small or retail investors, who contribute significantly to the daily exchange trading volumes, will receive funds or assets post-execution faster. This will bring various operational benefits and improve market risk mitigation.
However, the proposed shift will require significant investor education and resilience to overcome the negative market sentiment caused by affected broker businesses. Investors will grapple with the shorter period for trade settlement, and brokers will need substantial investments to update front-to-back-office systems. Moreover, the higher settlement costs could potentially disappoint investors.
Implications for banks and financial services institutions
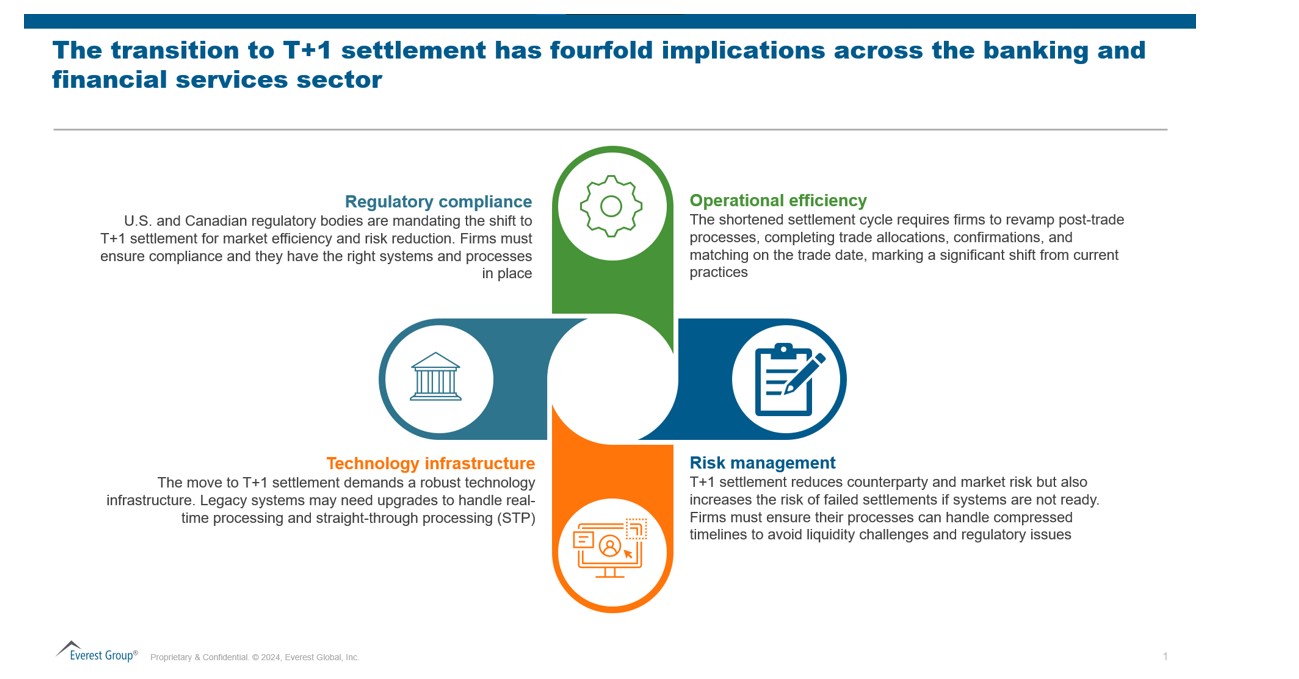
The shift to T+1 settlement presents a significant opportunity for the financial industry to enhance operational efficiencies and reduce risk. As Martin Palivec, Head of Securities Services, Canada, Citi, has highlighted, many post-trade processes still rely heavily on manual intervention, indicating a clear need for automation and streamlining. Settlement compression will drive the industry to strengthen and automate these processes, leading to more efficient and reliable operations.
Moreover, improving reporting capabilities is becoming increasingly critical, with clients expecting timeliness and accuracy in trade status updates. This underscores the urgency for organizations to adopt advanced technologies and modernize their post-trade infrastructure.
Role of IT and technology service providers
By partnering with IT and technology services providers, banks and financial institutions can navigate the complexities of T+1 settlement and position themselves for success in the evolving financial landscape.
IT and technology services providers can play a crucial role in assisting banks and financial services institutions in their T+1 journey in the following ways:
- System Upgrades and Integration: Technology providers can help firms upgrade their existing systems or integrate new systems to support T+1 settlement. This includes implementing real-time processing capabilities, enhancing data management systems, and ensuring interoperability with other market participants
- Automation and Straight-Through Processing: Automation is key to achieving operational efficiency in a T+1 settlement environment. Technology providers can assist firms in automating trade interfaces, matching and affirming trades in real time, and streamlining settlement workflows to minimize the risk of failed settlements
- Data Management and Reporting: Accurate and timely data management is critical with the compressed settlement timeline. Technology providers can help firms improve data quality, implement real-time reporting capabilities, and enhance communication with counterparties to reduce the risk of errors and delays
- Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management: Technology providers can assist firms in ensuring compliance with T+1-related regulatory requirements, including implementing systems to monitor and report trade status and manage risk factors associated with the new settlement cycle
The move to the T+1 settlement represents a significant advancement in the financial industry, necessitating operational and technological adjustments for banks and financial institutions.
As this transition unfolds, the prospect of T+0 settlement looms, with countries like India already making strides in this direction. The adoption of distributed ledger technology (DLT) is expected to be pivotal in enabling T+0 settlement and offering real-time, secure, and transparent transaction processing.
Organizations preparing for T+1 should also consider the potential shift to T+0 in their strategic planning. By embracing technologies and practices supporting T+1 and T+0 settlement, businesses can streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and stay ahead of the curve in an evolving financial landscape.
To learn more about the impact of T+1 settlements in the financial services industry, contact Abhinav Rathaur, [email protected], Kriti Seth, [email protected], and Pranati Dave, [email protected].
Read the blog, Beyond the Hype: Approaching Gen AI in BFSI Enterprises with the Generative AI-EXCEL Framework, to learn about successful gen AI adoption in the BFSI sector.